

 Tutorials Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
 Control Line Length by Image
Control Line Length by Image 
The sample input file used in the example is below.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface6.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map1.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
int unum = 50, vnum = 50;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < vnum; j++) {
double val = map.get( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt1 = surf.pt( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt2 = surf.pt( i*uinc, j*vinc, val*-10 );
new ICurve(pt1, pt2).clr(0);
}
}
}

 Control Depth of Surface by Image
Control Depth of Surface by Image  Here is an example to differentiate
offset depths of a vertex of panel.
Here is an example to differentiate
offset depths of a vertex of panel.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface7.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map1.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
int unum = 20, vnum = 20;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < vnum; j++) {
double val = map.get( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt11 = surf.pt( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt21 = surf.pt( (i+1)*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt12 = surf.pt( i*uinc, (j+1)*vinc, val*-4 );
IVec pt22 = surf.pt( (i+1)*uinc, (j+1)*vinc );
new ISurface(pt11, pt12, pt22, pt21).clr(.3);
}
}
surf.del();
}
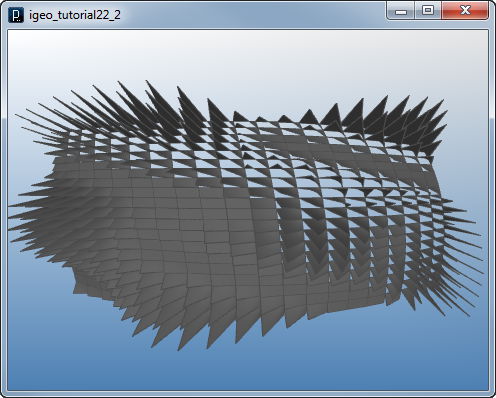
 Control Width of Panel by Image
Control Width of Panel by Image Here is an example to control the width of panel by
changing sampling location of the input surface with
the image value. The code below is control the width in v direction.
Here is an example to control the width of panel by
changing sampling location of the input surface with
the image value. The code below is control the width in v direction.
Here is the input bitmap used in the example.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface7.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map1.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
int unum = 20, vnum = 20;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < vnum; j++) {
double val = map.get( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt11 = surf.pt( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt21 = surf.pt( (i+1)*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt12 = surf.pt( i*uinc, (j + val)*vinc );
IVec pt22 = surf.pt( (i+1)*uinc, (j + val)*vinc );
new ISurface(pt11, pt12, pt22, pt21).clr(.3);
}
}
surf.del();
}
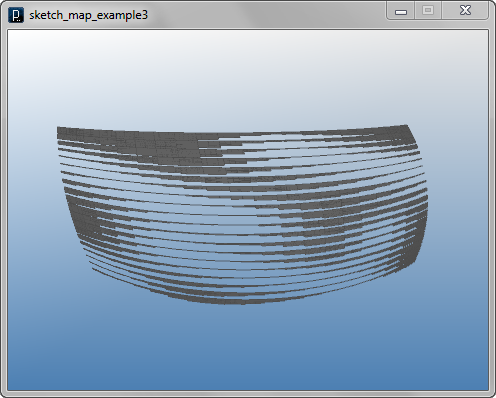
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface7.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map1.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
int unum = 20, vnum = 20;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < vnum; j++) {
double val = map.get( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt11 = surf.pt( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt21 = surf.pt( (i + val)*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt12 = surf.pt( i*uinc, (j + 1)*vinc );
IVec pt22 = surf.pt( (i + val )*uinc, (j + 1)*vinc );
new ISurface(pt11, pt12, pt22, pt21).clr(.3);
}
}
surf.del();
}

 Control Rotation by Image
Control Rotation by Image  Here is an example to rotate panelized surfaces by sampled values of the image.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
Here is an example to rotate panelized surfaces by sampled values of the image.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface7.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map1.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
int unum = 20, vnum = 20;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < vnum; j++) {
double val = map.get( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt11 = surf.pt( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt21 = surf.pt( (i + 1)*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt12 = surf.pt( i*uinc, (j + (1-val) )*vinc );
IVec pt22 = surf.pt( (i + 1)*uinc, (j + (1-val) )*vinc );
ISurface panel = new ISurface(pt11, pt12, pt22, pt21).clr(.2);
IVec center = surf.pt( (i+0.5)*uinc, (j+0.5)*vinc );
IVec normal = surf.nml( (i+0.5)*uinc, (j+0.5)*vinc );
panel.rot(center, normal, val*PI/4 );
}
}
surf.del();
}

 Control Scaling by Image
Control Scaling by Image Here is an example to scale panelized surfaces by sampled values of the image.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
Here is an example to scale panelized surfaces by sampled values of the image.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface7.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map1.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
int unum = 40, vnum = 40;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < vnum; j++) {
double val = map.get( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt11 = surf.pt( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt21 = surf.pt( (i + 1)*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt12 = surf.pt( i*uinc, (j + 1)*vinc );
IVec pt22 = surf.pt( (i + 1)*uinc, (j + 1)*vinc );
ISurface panel = new ISurface(pt11, pt12, pt22, pt21).clr(.2);
IVec center = surf.pt( (i+0.5)*uinc, (j+0.5)*vinc );
// val is inverted by subtraction
panel.scale(center, 1 - val );
}
}
surf.del();
}

 Sampling Color of Image
Sampling Color of Image Here is an example to use color of the image with the clr()
method of IImageMap class.
When the image is full color image, the value returned by get()
method is a gray scale value when the color is converted into gray.
Here is an example to use color of the image with the clr()
method of IImageMap class.
When the image is full color image, the value returned by get()
method is a gray scale value when the color is converted into gray.
The input bitmap used in the example is this.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.open("surface7.3dm");
ISurface[] surfaces = IG.surfaces();
IImageMap map = new IImageMap("map2.jpg");
for (ISurface surf : surfaces) {
int unum = 40, vnum = 40;
double uinc = 1.0/unum, vinc = 1.0/vnum;
for (int i=0; i < unum; i++) {
for (int j=0; j < vnum; j++) {
double val = map.get( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt11 = surf.pt( i*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt21 = surf.pt( (i + 1)*uinc, j*vinc );
IVec pt12 = surf.pt( i*uinc, (j + 1)*vinc, val*-4 );
IVec pt22 = surf.pt( (i + 1)*uinc, (j + 1)*vinc );
ISurface panel = new ISurface(pt11, pt12, pt22, pt21);
panel.clr(map.clr( i*uinc, j*vinc ));
}
}
surf.del();
}


 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
