

 チュートリアル チュートリアル | (トピック一覧へ戻る) |
 インタラクト・メソッドの定義
インタラクト・メソッドの定義![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
MyAgent agent = new MyAgent();
}
class MyAgent extends IAgent{
void interact(ArrayList< IDynamics > agents){
// definition of interact behavior
}
void update(){
// definition of update behavior
}
}
interactには他ののエージェントとの相互作用のための 任意の処理が記述できます。 同じクラスのエージェントとの相互作用を記述する場合は以下のようになります。
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
MyAgent agent = new MyAgent();
}
class MyAgent extends IAgent{
void interact(ArrayList< IDynamics > agents){
for(int i=0; i < agents.size(); i++){ //check all existing agents
if(agents.get(i) instanceof MyAgent){ //type check
MyAgent agent = (MyAgent)agents.get(i); //casting type
if(agent!= this){ //agents include this instance itself
// definition of interact behavior
}
}
}
}
void update(){
// definition of update behavior
}
}
メソッドのヘッダは以下のように定義され、
Forループによってカウンタ変数iの値を0からエージェントの数
agents.size()-1まで反復します。
for(int i=0; i < agents.size(); i++){
個々のエージェントを参照するには、カウンタ変数iとArrayListのgetメソッド を用います。 agents.get(i) 以下のif条件分岐で、参照しているi番目のエージェントが MyAgentのインスタンスであることを確認します。 引数のagentsにはすべてのエージェントが入っているので それがMyAgentのものとは限らないためです。 instanceof演算子は左項にオブジェクトとり、 それが右側のクラスかその子クラスのインスタンスである場合に真(true)を返します。
if(agents.get(i) instanceof MyAgent){
i番目のエージェントのオブジェクト型を MyAgentの型に変換(キャスト)して、 変数agentに代入します。 オブジェクトの型を変換するには 変数名の左側でクラス名を括弧で囲みます。 もし指定のオブジェクトが指定の型に属さない場合は例外が発生します。 型変換に関する詳細については Javaの公式ドキュメントを参照してください。
MyAgent agent = (MyAgent)agents.get(i);
agentsはすべてのエージェントが含まれるため、 interactを実行しているエージェント自身も含まれます。 以下のIf条件分岐で agentのエージェントが実行中のエージェントでないことを確認します。 キーワードthisが実行中のエージェントを参照します。
if(agent!= this){
 インタラクト・メソッドの定義 : 短縮版
インタラクト・メソッドの定義 : 短縮版![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
MyAgent agent = new MyAgent();
}
class MyAgent extends IAgent{
void interact(IDynamics agent){
if(agent instanceof MyAgent){ //type check
MyAgent myAgent = (MyAgent)agent; //casting type
// definition of interact behavior
}
}
void update(){
// definition of update behavior
}
}
引数には、各アップデート・サイクルにおいて、 実行中のエージェント自身を除く、 存在するすべてのエージェントがひとつずつ渡されます。 ただし、このメソッドはArrayListを引数に取る上記のメソッドに比べて 実行速度が遅くなります。 また、複数エージェントを同時に参照する処理もできません。 そのため、実行速度が求められる場合や複数のエージェントを参照して処理をする必要のあるときは ArrayListを引数に取るinteractメソッドを使用してください。
 インタラクト・メソッドの例その1
インタラクト・メソッドの例その1
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.duration(120);
LineAgent agent =
new LineAgent(new IVec(0,0,0), new IVec(1,0,0));
}
static class LineAgent extends IAgent{
static double length = 2;
static double clearance = 1.99; //less than length
IVec pt1, pt2;
boolean isColliding=false;
LineAgent(IVec pt, IVec dir){
pt1 = pt;
pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(length));
}
void interact(IDynamics agent){
if(time == 0){ //only in the first time
if(agent instanceof LineAgent){
LineAgent lineAgent = (LineAgent)agent;
// checking clearance of end point
if(lineAgent.pt2.dist(pt2) < clearance){
isColliding=true;
}
}
}
}
void update(){
if(isColliding){
del();
}
else if(time == 0){ //if not colliding
new ICurve(pt1,pt2).clr(0);
IVec dir = pt2.dif(pt1);
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis, PI/3));
}
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend the other way
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis, -PI/3));
}
if(IRandom.percent(80)){ //straight
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup());
}
}
}
}
このインタラクト・メソッドは、エージェント間の距離を条件として処理を分岐しています。
if(lineAgent.pt2.dist(pt2) < clearance){
エージェント間の距離が変数clearanceよりも小さい場合、 ブーリアン変数isCollidingがtrueに設定されます。 isCollidingがtrueであると、 アップデート・メソッドにおいて、このエージェントは削除されます。 falseである場合は新しいエージェントが ランダムに選んだ正面、60°、-60°のいずれかの方向に生成されます。 この処理を以下の図に示します。

インタラクト・メソッドでの距離を調べることによる衝突判定と、 アップデート・メソッドでの子エージェントの生成は、 if条件 if(time == 0){により エージェントが生成してからの最初のフレームで一度だけ行われます。 変数timeはIAgentクラスのフィールドであり、自身の生成から現在までの アップデートサイクルの数をカウントします。
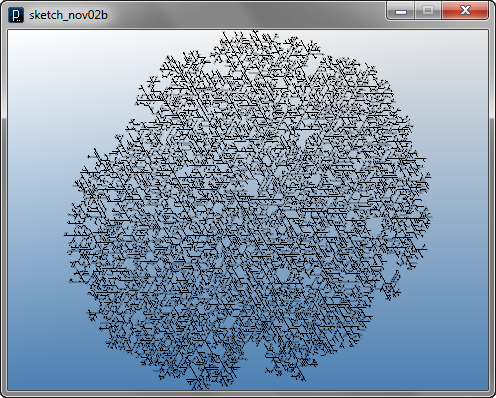

以下のコードでは上記の動作を ArrayListを引数に取るinteract()メソッドを用いて書き直し、 実行速度の向上を図っています。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.duration(120);
LineAgent agent =
new LineAgent(new IVec(0,0,0), new IVec(1,0,0));
}
static class LineAgent extends IAgent{
static double length = 2;
static double clearance = 1.99; //less than length
IVec pt1, pt2;
boolean isColliding=false;
LineAgent(IVec pt, IVec dir){
pt1 = pt;
pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(length));
}
void interact(ArrayList< IDynamics > agents){
if(time == 0){ //only in the first time
for(int i=0; i < agents.size(); i++){
if(agents.get(i) instanceof LineAgent){
LineAgent lineAgent = (LineAgent)agents.get(i);
if(lineAgent != this){
// checking clearance of end point
if(lineAgent.pt2.dist(pt2) < clearance){
isColliding=true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
void update(){
if(isColliding){
del();
}
else if(time == 0){ //if not colliding
new ICurve(pt1,pt2).clr(0);
IVec dir = pt2.dif(pt1);
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis, PI/3));
}
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend the other way
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis, -PI/3));
}
if(IRandom.percent(80)){ //straight
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup());
}
}
}
}
 インタラクト・メソッドの例その2
インタラクト・メソッドの例その2ランダムな角度は正面方向からPI/3とPI/3*2の間で選ばれる必要があります。 もし角度がPI/3以下であると、正面のエージェントと衝突し得ます。 PI/3*2以上であれば、lengthフィールドとclearanceフィールドの値によっては 親エージェントと衝突し得ます。 また、子エージェントが親エージェントと常に衝突することを避けるため、 lengthの値はclearanceの値よりすこし小さくしてあります。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.duration(250);
LineAgent agent =
new LineAgent(new IVec(0,0,0), new IVec(1,0,0));
}
static class LineAgent extends IAgent{
static double length = 2;
static double clearance = 1.99; //less than length
IVec pt1, pt2;
boolean isColliding=false;
LineAgent(IVec pt, IVec dir){
pt1 = pt;
pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(length));
}
void interact(IDynamics agent){
if(time == 0){ //only in the first time
if(agent instanceof LineAgent){
LineAgent lineAgent = (LineAgent)agent;
// checking clearance of end point
if(lineAgent.pt2.dist(pt2) < clearance){
isColliding=true;
}
}
}
}
void update(){
if(isColliding){
del();
}
else if(time == 0){ //if not colliding
new ICurve(pt1,pt2).clr(0);
IVec dir = pt2.dif(pt1);
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis,
IRandom.get(PI/3,PI/3*2)));
}
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend the other way
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis,
-IRandom.get(PI/3,PI/3*2)));
}
if(IRandom.percent(80)){ //straight
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup());
}
}
}
}
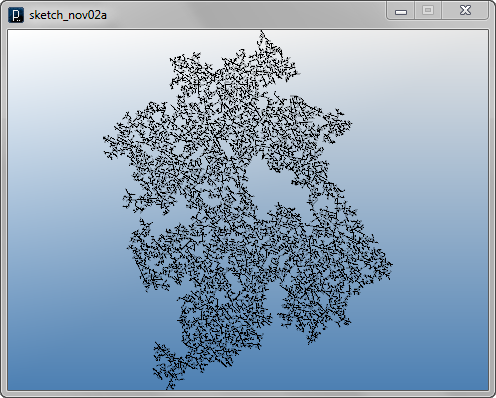
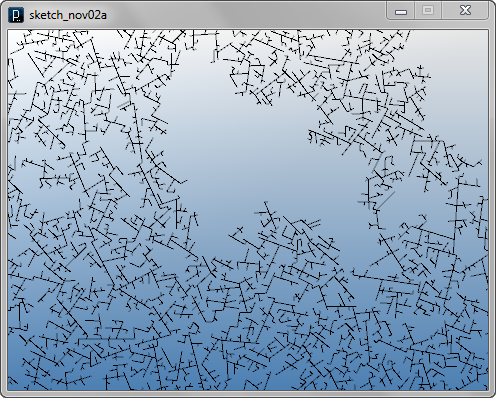
 インタラクト・メソッドの例その3
インタラクト・メソッドの例その3![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.duration(150);
new LineAgent(new IVec(0,0,0), new IVec(1,0,0));
}
static class LineAgent extends IAgent{
static double length = 2;
static double clearance = 1.99; //less than length
IVec pt1, pt2;
boolean isColliding=false;
LineAgent(IVec pt, IVec dir){
pt1 = pt;
pt2 = pt.dup().add(dir.dup().len(length));
}
void interact(IDynamics agent){
if(time == 0){ //only in the first time
if(agent instanceof LineAgent){
LineAgent lineAgent = (LineAgent)agent;
// checking clearance of end point
if(lineAgent.pt2.dist(pt2) < clearance){
isColliding=true;
}
}
}
}
void update(){
if(isColliding){
del();
}
else if(time == 0){ //if not colliding
new ICurve(pt1,pt2).clr(0);
IVec dir = pt2.dif(pt1);
//rotation axis with random direction
IVec axis = IRandom.pt(-1,1).len(1);
if(IRandom.percent(50)){ //bend
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(axis,
IRandom.get(PI/3,PI/3*2)));
}
if(IRandom.percent(50)){ //bend the other way
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(axis,
-IRandom.get(PI/3,PI/3*2)));
}
if(IRandom.percent(80)){ //straight
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup());
}
}
}
}

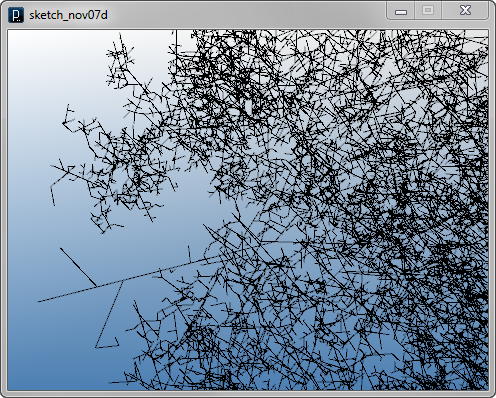
 インタラクト・メソッドの例その4
インタラクト・メソッドの例その4![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480,360,IG.GL);
IG.duration(400);
new MySphereAgent(IRandom.pt(-10,10),IRandom.get(5,20));
new MySphereAgent(IRandom.pt(-10,10),IRandom.get(5,20));
IG.fill();
}
class MySphereAgent extends IAgent{
IVec pos;
double radius;
ISphere sphere;
boolean changed=true;
MySphereAgent(IVec p, double rad){
pos = p;
radius = rad;
}
void interact(IDynamics agent){
if(agent instanceof MySphereAgent){
MySphereAgent sa = (MySphereAgent)agent;
double dist = sa.pos.dist(pos);
if(dist < radius+sa.radius){
IVec dif = pos.dif(sa.pos);
//amount of overlap is this radius plus other radius minus distance between two centers
dif.len(radius+sa.radius-dist);
pos.add(dif); //only this agent is moved, not others
changed=true; //state variable is updated
}
}
}
void update(){
if(changed){
// update sphere
if(sphere!=null) sphere.del(); //shpere is null first
sphere = new ISphere(pos, radius).clr(clr());
changed=false;
}
if(time==5){ //delayed to create the next agent til time==5
// next agent's direction
IVec dir = IRandom.pt(-1, 1);
double nextRadius = IRandom.get(5, 20);
// amount of move is the current radius + the next one
dir.len(radius+nextRadius);
new MySphereAgent(pos.cp(dir),nextRadius).clr(IRandom.clr());
}
}
}
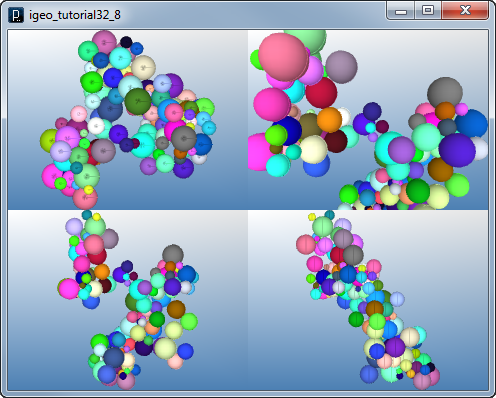
 インタラクト・メソッドの例その5
インタラクト・メソッドの例その5![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup() {
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.duration(500);
int num=20;
for (int i=0; i < num; i++) {
new RectAgent(IRandom.pt(-100,-100, 0,100,100, 0),
20, 20).clr(IRandom.clr());
}
}
static class RectAgent extends IAgent {
static double gap = 1.0;
static double minSize = 1.0;
static double maxSize = 20.0;
IVec pos;
double width, height;
boolean anyChange=true;
ISurface rect;
RectAgent(IVec pt, double w, double h) {
pos = pt;
width=w;
height=h;
}
void interact(IDynamics agent) {
// shrink the size when it collides with others.
if (agent instanceof RectAgent) {
RectAgent ra = (RectAgent) agent;
// is it overlapping?
if (ra.pos.x+ra.width+gap > pos.x &&
ra.pos.x < pos.x + width+gap &&
ra.pos.y+ra.height+gap > pos.y &&
ra.pos.y < pos.y + height+gap) {
// both x and y overlapping?
if (ra.pos.x >= pos.x && ra.pos.y >= pos.y) {
if ( ra.pos.x - pos.x > ra.pos.y - pos.y ) {
width = ra.pos.x - pos.x - gap;
}
else {
height = ra.pos.y - pos.y - gap;
}
anyChange = true;
}
// x is right of pos
else if (ra.pos.x > pos.x) {
width = ra.pos.x - pos.x - gap;
anyChange = true;
}
// y is top of pos
else if (ra.pos.y > pos.y) {
height = ra.pos.y - pos.y - gap;
anyChange = true;
}
}
}
}
void update() {
// update geometry only when the size changes
if (anyChange) {
if (rect != null) rect.del();
if (width >= minSize && height >= minSize) {
rect = IG.plane(pos, width, height).clr(clr());
}
// if too small, removed
else { del(); }
anyChange=false;
}
if (time==0) {
new RectAgent(pos.cp(IRandom.pt(-10,-10, 0,10,10, 0)),
IRandom.get(minSize,maxSize),
IRandom.get(minSize,maxSize)).clr(clr());
}
}
}

 インタラクト・メソッドの例その6
インタラクト・メソッドの例その6![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup() {
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.duration(100);
new MyAutomaton(new IVec(0, 0, 0));
}
static class MyAutomaton extends IAgent {
static double size = 10;
IVec pos;
int state = 1;
MyAutomaton leftAutomaton=null, rightAutomaton=null;
int lstate = 0, rstate = 0;
MyAutomaton(IVec p) { pos = p; }
void interact(IDynamics agent){
int leftState=0, rightState=0;
//searching left and right automaton
//if not found leftState & rightState are zero
if(agent instanceof MyAutomaton){
MyAutomaton automaton = (MyAutomaton)agent;
if(automaton.pos.eqX(pos.dup().sub(size,0,0))){
leftAutomaton = automaton;
lstate = leftAutomaton.state;
}
else if(automaton.pos.eqX(pos.dup().add(size,0,0))){
rightAutomaton = automaton;
rstate = rightAutomaton.state;
}
}
}
void update() {
// when state==1, put a box, otherwise no box
if(state == 1){
new IBox(pos.dup(), size, size, size).clr(0);
}
// update state with a state transition table
if(lstate==0 && state==0 && rstate==0){ state=0; }
else if(lstate==0 && state==0 && rstate==1){ state=1; }
else if(lstate==0 && state==1 && rstate==0){ state=1; }
else if(lstate==0 && state==1 && rstate==1){ state=1; }
else if(lstate==1 && state==0 && rstate==0){ state=1; }
else if(lstate==1 && state==0 && rstate==1){ state=0; }
else if(lstate==1 && state==1 && rstate==0){ state=0; }
else if(lstate==1 && state==1 && rstate==1){ state=0; }
//move down
pos.add(0,-size,0);
//new automaton
if(leftAutomaton==null){
new MyAutomaton(pos.dup().sub(size,0,0));
}
if(rightAutomaton==null){
new MyAutomaton(pos.dup().add(size,0,0));
}
}
}


 インタラクト・メソッドの例その7
インタラクト・メソッドの例その7![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.duration(250);
new LineAgent(new IVec(0,0,0), new IVec(0,1,0)).clr(0);
}
static class LineAgent extends IAgent{
IVec pt1, pt2;
boolean isColliding=false;
LineAgent(IVec pt, IVec dir){
pt1 = pt;
pt2 = pt.cp(dir);
}
void interact(ArrayList< IDynamics > agents){
if(time == 0){ //only in the first time
for(int i=0; i < agents.size() && !isColliding; i++){
if(agents.get(i) instanceof LineAgent){
LineAgent a = (LineAgent)agents.get(i);
if(a != this){
if(!a.isColliding){
IVec intxn = IVec.intersectSegment(pt1, pt2,
a.pt1,a.pt2);
if(intxn!=null){ //intersection exists
if(!intxn.eq(pt1)){ //not parent agent
isColliding=true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
void update(){
if(isColliding){
del();
}
else if(time == 0){ //if not colliding
new ICurve(pt1,pt2).clr(clr());
IVec dir = pt2.dif(pt1);
double r = red()+IRand.get(0,0.01);
double g = green()+IRand.get(0,0.01);
double b = blue()+IRand.get(0,0.01);
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis,
IRandom.get(0,PI/20))).clr(r,g,b);
}
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend the other way
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis,
-IRandom.get(0,PI/20))).clr(r,g,b);
}
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //straight
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup()).clr(r,g,b);
}
}
}
}
このコードでは、衝突判定を線分の交点を計算する
IVec.intersectSegment(line1Pt1, line1Pt2, line2Pt1, line2Pt2)
メソッドを用いて行います。
このメソッドは、与えられた2つの線分が交差する点をIVecオブジェクトとして返すか、 交差していない場合はnullを返します。 また、長さが無限の直線の交点を計算するメソッドもあります。 IVec.intersect(line1Pt1, line1Pt2, line2Pt1, line2Pt2);
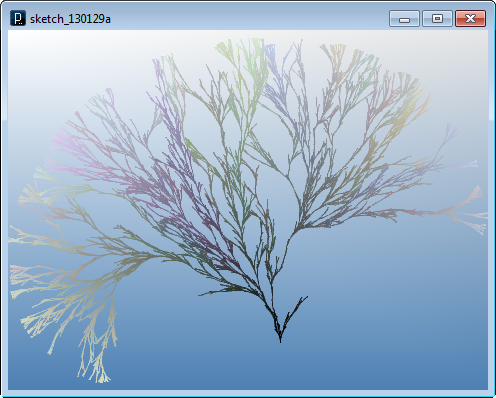
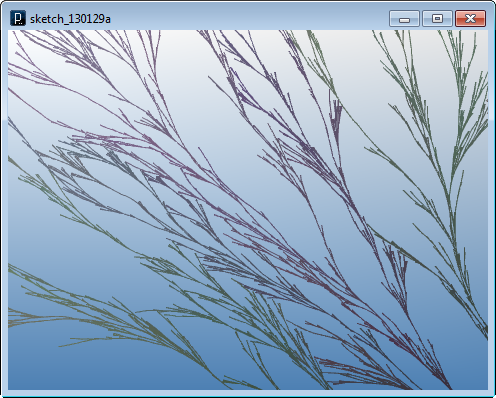
上記のメソッドは3次元空間の線を取り扱います。
2線の交点が"IConfig.tolerance"に定義される許容差を満たさなければnullを返します。
線が2次元空間に存在する場合、IVec2クラスに定義されている同名のメソッドも利用できます。
IVec2.intersectSegment(line1Pt1, line1Pt2, line2Pt1, line2Pt2)
この場合、メソッドの引数にはIVec2クラスを用います。
IVecオブジェクトからはto2d()メソッドを用いて変換します。
逆にIVec2からIVecへ変換するにはto3d()メソッドが利用できます。
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
import processing.opengl.*;
import igeo.*;
void setup(){
size(480, 360, IG.GL);
IG.duration(250);
new LineAgent(new IVec(0,0,0), new IVec(0,1,0)).clr(0);
}
static class LineAgent extends IAgent{
IVec pt1, pt2;
boolean isColliding=false;
LineAgent(IVec pt, IVec dir){
pt1 = pt;
pt2 = pt.cp(dir);
}
void interact(ArrayList< IDynamics > agents){
if(time == 0){ //only in the first time
for(int i=0; i < agents.size() && !isColliding; i++){
if(agents.get(i) instanceof LineAgent){
LineAgent a = (LineAgent)agents.get(i);
if(a != this){
if(!a.isColliding){
IVec2 intxn =
IVec2.intersectSegment(pt1.to2d(),pt2.to2d(),
a.pt1.to2d(),a.pt2.to2d());
if(intxn!=null){ //intersection exists
if(!intxn.eq(pt1.to2d())){ //not parent agent
isColliding=true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
void update(){
if(isColliding){
del();
}
else if(time == 0){ //if not colliding
new ICurve(pt1,pt2).clr(clr());
IVec dir = pt2.dif(pt1);
double r = red()+IRand.get(0,0.01);
double g = green()+IRand.get(0,0.01);
double b = blue()+IRand.get(0,0.01);
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis,
IRandom.get(0,PI/20))).clr(r,g,b);
}
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //bend the other way
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup().rot(IG.zaxis,
-IRandom.get(0,PI/20))).clr(r,g,b);
}
if(IRandom.percent(40)){ //straight
new LineAgent(pt2, dir.dup()).clr(r,g,b);
}
}
}
}
 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
