

 Python Tutorials Python Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
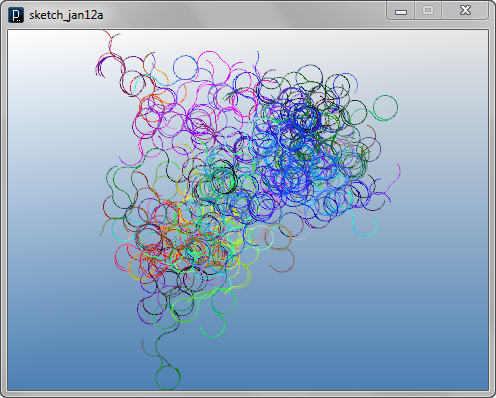
 Multi-Agent 2D Example 3 (requires iGeo version 7.5.1 or higher)
Multi-Agent 2D Example 3 (requires iGeo version 7.5.1 or higher)![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(700)
# left 99.0%, right 1.5%
LineAgent(IG.v(0,0,0), IG.v(2,0,0), 99.0, 1.5).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir, pctL, pctR) :
self.pos = pt
self.dir = dir
self.pctL = pctL
self.pctR = pctR
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
#putting line geometry
pos2 = self.pos.dup().add(self.dir)
ICurve(self.pos, pos2).clr(self.clr())
r = self.red() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
g = self.green() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
b = self.blue() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
if IRand.pct(3.0) : #swap L/R percent
tmp = self.pctL
self.pctL = self.pctR
self.pctR = tmp
if IRand.pct(self.pctL) : #bend left
dir2 = self.dir.dup()
dir2.rot(PI/30)
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctL, self.pctR).clr(r,g,b)
if IRand.pct(self.pctR) : #bend right
dir2 = self.dir.dup()
dir2.rot(-PI/30)
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctL, self.pctR).clr(r,g,b)
self.del()
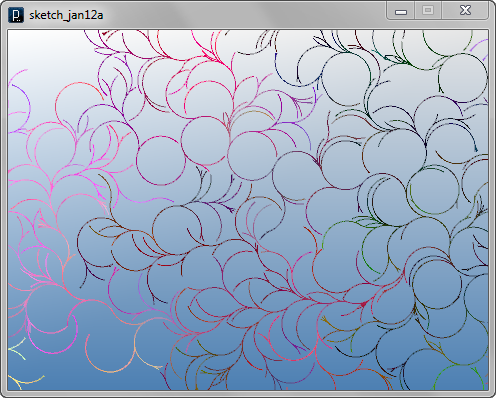
The next code adds interact() method to the previous code to detect collision of line agents. A line agent stops when it collides into other existing agents. Then the algorithm to swap left and right probability is also changed to swap them only when an agent creates a new branch.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(350)
# left 99.0%, right 7.0%
LineAgent(IG.v(0,0,0), IG.v(2,0,0), 99.0, 7.0).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir, pctL, pctR) :
self.pos = pt
self.dir = dir
self.pctL = pctL
self.pctR = pctR
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time()==0 :
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) and agent is not self :
if agent.pos.dist(self.pos.cp(self.dir)) < self.dir.len()*0.999 :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
return
#putting line geometry
pos2 = self.pos.dup().add(self.dir)
ICurve(self.pos, pos2).clr(self.clr())
r = self.red() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
g = self.green() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
b = self.blue() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
branchL = IRand.pct(self.pctL) #boolean switch L
branchR = IRand.pct(self.pctR) #boolean switch R
if branchL : #bend left
dir2 = self.dir.dup()
dir2.rot(PI/30)
if branchR and self.pctR > self.pctL :#swap L/R% when branching both
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctR, self.pctL).clr(r,g,b)
else :
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctL, self.pctR).clr(r,g,b)
if branchR : #bend right
dir2 = self.dir.dup()
dir2.rot(-PI/30)
if branchL and self.pctR < self.pctL :#swap L/R% when branching both
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctR, self.pctL).clr(r,g,b)
else :
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctL, self.pctR).clr(r,g,b)

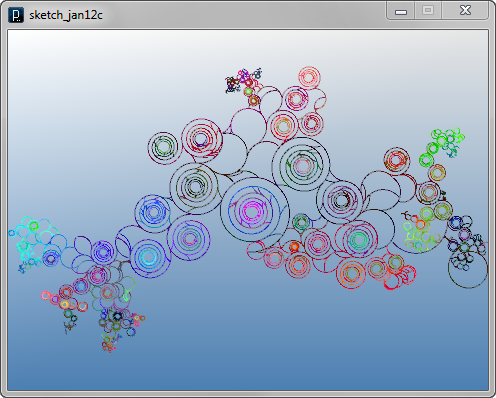
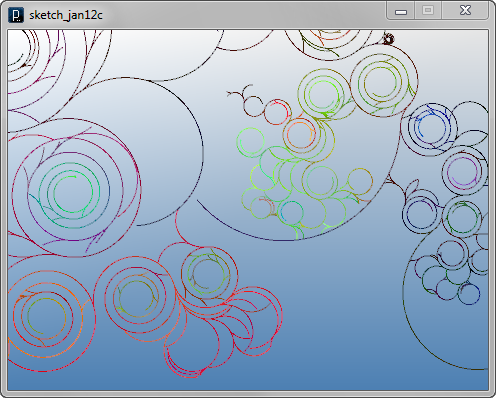
The code below
changes the length of agent's line at every update.
The lengths of all agents are slightly scaled down
constantly, creating swirling curves.
On top of it, the length is scaled up or down stochastically,
only when the agent is creating a branch.
In intersect() method, the
collision detection algorithm is changed.
It's using the method of
IVec.intersectLine(IVec line1Pt1, IVec line1Pt2, IVec line2Pt1, IVec line2Pt2)
to calculate intersection of two line segments because
the previous algorithm of collision detection wouldn't work
when there are different lengths of lines.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(400)
# left 100%, right 4.5%
LineAgent(IG.v(0,0,0), IG.v(2,0,0), 100, 4.5).clr(0)
class LineAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir, pctL, pctR) :
self.pos = pt
self.dir = dir
self.pctL = pctL
self.pctR = pctR
self.isColliding = False
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time()==0 :
for agent in agents :
if self.isColliding :
return
if isinstance(agent, LineAgent) and agent is not self :
pos2 = self.pos.cp(self.dir)
apos2 = agent.pos.cp(agent.dir)
# not sharing root and intersecting
if not apos2.eq(self.pos) and not agent.pos.eq(self.pos) and \
IVec.intersectLine(agent.pos,apos2,self.pos,pos2) is not None :
self.isColliding=True
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
if self.isColliding :
self.del()
return
pos2 = self.pos.dup().add(self.dir)
ICurve(self.pos, pos2).clr(self.clr())
r = self.red() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
g = self.green() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
b = self.blue() + IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
branchL = IRand.pct(self.pctL)
branchR = IRand.pct(self.pctR)
lenL = self.dir.len()
lenR = self.dir.len()
lenL*=0.995 #shrinking length
lenR*=0.995 #shrinking length
if branchL and branchR : #only when branching both
if IRand.pct(50) :
if self.pctL < self.pctR :
lenL *= 0.9
else :
lenR *= 0.9
elif IRand.pct(6.0) :
if self.pctL < self.pctR :
lenL *= 0.4
else :
lenR *= 0.4
elif IRand.pct(5.0) :
if self.pctL < self.pctR :
lenL *= 4.0
else :
lenR *= 4.0
if branchL : #bend left
dir2 = self.dir.dup()
dir2.len(lenL) #update length
dir2.rot(PI/30)
if branchR and self.pctR > self.pctL : #swap L/R% when branching both
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctR, self.pctL).clr(r,g,b)
else :
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctL, self.pctR).clr(r,g,b)
if branchR : #bend right
dir2 = self.dir.dup()
dir2.len(lenR) #update length
dir2.rot(-PI/30)
if branchL and self.pctR < self.pctL : #swap L/R% when branching both
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctR, self.pctL).clr(r,g,b)
else :
LineAgent(pos2, dir2, self.pctL, self.pctR).clr(r,g,b)

 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
