

 Python Tutorials Python Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
 Swarm Example 2 (requires iGeo version 7.6.0 or higher)
Swarm Example 2 (requires iGeo version 7.6.0 or higher)The first code below describes a swarm agent class MyBoid and this agent draws profile polygon lines around the agent's position instead of drawing trace lines behind. The number of vertices of the polygon lines is defined by the variable of pointNum in MyBoid class. Each vertex of the polygon is calculated by rotating points around the velocity vector of the agent.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(170)
num = 16
for i in range(num) :
#circular configuration
MyBoid(IG.v(80,0,0).rot(PI*2/num*i), \
IG.v(-IRand.get(20,40),0,i%2*20-10).rot(PI*2/num*i+PI/4)).fric(0.001).clr(IRand.gray())
Attractor(IG.v(0,0,0))
class MyBoid(IBoid) :
def __init__(self, p, v) :
IBoid.__init__(self,p,v)
self.cohesionDist(60)
self.cohesionRatio(5)
self.separationDist(50)
self.separationRatio(8)
self.alignmentDist(40)
self.alignmentRatio(0)
def update(self) : #drawing line
radius = 3
pointNum = 5
points = []
for i in range(pointNum) :
axis = self.vel().cross(IG.zaxis)
axis.len(radius)
axis.rot(self.vel(), 2*PI/pointNum*i)
points.append(self.pos().cp(axis))
for i in range(pointNum) :
ICurve(points[i], points[(i+1)%pointNum]).clr(self.clr())
class Attractor(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p) :
self.pos = p
def interact(self, agents) :
attraction = 0.4
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyBoid) :
frc = agent.pos().dif(self.pos).mul(attraction)
agent.pull(frc)

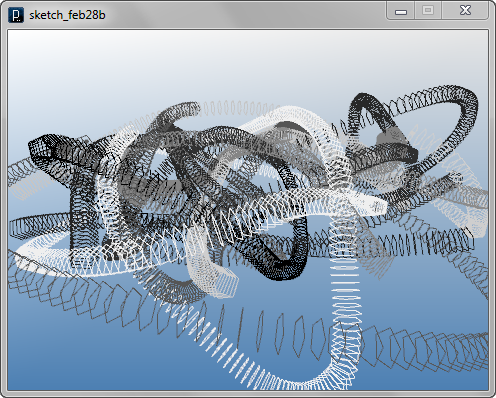
The next code controls the radius of polygon by time and connects profile polygon lines with diagonal lines creating truss connections.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(170)
num = 16
for i in range(num) :
#circular configuration
MyBoid(IG.v(80,0,0).rot(PI*2/num*i), \
IG.v(-IRand.get(20,40),0,i%2*20-10).rot(PI*2/num*i+PI/4)).fric(0.001).clr(IRand.gray())
Attractor(IG.v(0,0,0))
class MyBoid(IBoid) :
def __init__(self, p, v) :
IBoid.__init__(self,p,v)
self.prevPoints = None
self.cohesionDist(60)
self.cohesionRatio(5)
self.separationDist(50)
self.separationRatio(8)
self.alignmentDist(40)
self.alignmentRatio(0)
def update(self) : #drawing line
radius = sin(IG.time()*0.1)*2 + 3 #changing radius by time
pointNum = 5
points = []
for i in range(pointNum) :
axis = self.vel().cross(IG.zaxis)
axis.len(radius)
axis.rot(self.vel(), 2*PI/pointNum*i)
points.append(self.pos().cp(axis))
if self.prevPoints is not None :
for i in range(pointNum) :
ICurve(points[i], points[(i+1)%pointNum]).clr(self.clr())
ICurve(points[i], self.prevPoints[(i+1)%pointNum]).clr(self.clr())
ICurve(points[i], self.prevPoints[i]).clr(self.clr())
self.prevPoints = points
class Attractor(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p) :
self.pos = p
def interact(self, agents) :
attraction = 0.4
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyBoid) :
frc = agent.pos().dif(self.pos).mul(attraction)
agent.pull(frc)
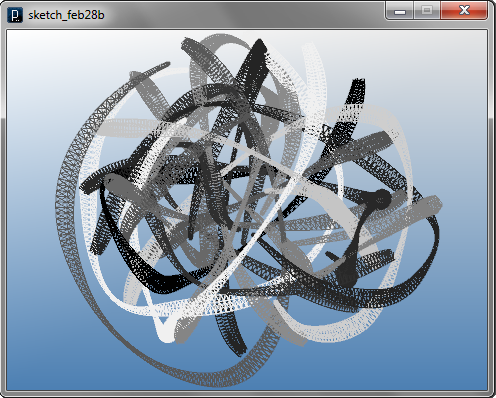
The code below shows an algorithm to interconnect
trajectories of swarm agents.
The swarm agent draws lines not only to other swarm agents' position
but also to the past trajectories of other agents.
To keep the information of past trajectories, a new agent class
Anchor is introduced.
Each swarm agent of MyBoid class puts an instance of Anchor
at its position of the moment.
This Anchor agent stays at the position checking other
swarm agents and if other agents are coming close enough,
it draws lines to them.
This check of other swarm agents is done by this line.
if(boid!=parent && dist < 18 && dist > 8 ){
It checks if it's not the parent swarm agent and if the distance is
smaller than 18 and also larger than 8 (not to draw too short lines),
the Anchor agent draws a line
to the MyBoid agent.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(170)
IG.bg(0)
num = 16
for i in range(num) :
#circular configuration
MyBoid(IG.v(80,0,0).rot(PI*2/num*i), \
IG.v(-IRand.get(20,40),0,i%2*20-10).rot(PI*2/num*i+PI/4)).fric(0.001).clr(IRand.gray(48))
Attractor(IG.v(0,0,0))
class Anchor(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, b) :
self.parent = b
self.pos = b.pos().cp()
def interact(self, agents) :
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyBoid) :
dist = agent.pos().dist(self.pos)
if agent is not self.parent and dist < 18 and dist > 8 :
ICurve(agent.pos().cp(), self.pos).clr(self.parent.clr())
class MyBoid(IBoid) :
def __init__(self, p, v) :
IBoid.__init__(self,p,v)
self.prevPos = None
self.cohesionDist(60)
self.cohesionRatio(5)
self.separationDist(50)
self.separationRatio(8)
self.alignmentDist(40)
self.alignmentRatio(0)
def update(self) : #drawing line
Anchor(self) #leaving an anchor behind
curPos = self.pos().cp()
if self.prevPos is not None :
ICurve(self.prevPos, curPos).clr(self.clr())
self.prevPos = curPos
class Attractor(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p) :
self.pos = p
def interact(self, agents) :
attraction = 0.4
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyBoid) :
frc = agent.pos().dif(self.pos).mul(attraction)
agent.pull(frc)

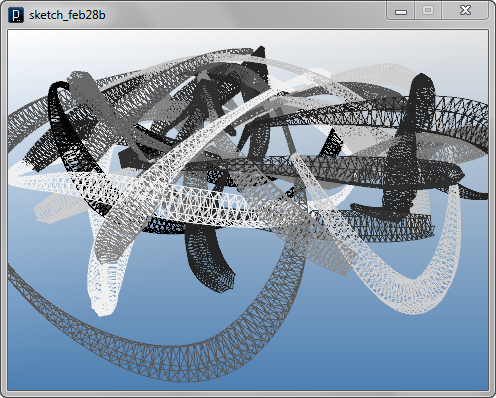
The code below combines the algorithm to create polygon truss geometries and the another algorithm to interconnect trajectories of swarm agents. The connection line of trajectories are drawn from the vertices of the truss geometries and the line is drawn as a closed polygon mesh geometry by the method IG.meshSquareStick(pt1, pt2, size).
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.duration(170)
IG.bg(0)
num = 16
for i in range(num) :
#circular configuration
MyBoid(IG.v(80,0,0).rot(PI*2/num*i), \
IG.v(-IRand.get(20,40),0,i%2*20-10).rot(PI*2/num*i+PI/4)).fric(0.001).clr(IRand.gray(48))
Attractor(IG.v(0,0,0))
class Anchor(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, b) :
self.parent = b;
self.pos = b.pos().cp()
self.points = b.points
def interact(self, agents) :
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyBoid) :
dist = agent.pos().dist(self.pos)
if agent is not self.parent and dist < 18 and dist > 8 :
meshSize = 0.5
r = sin(IG.time()*0.1)*0.1+0.3
g = 0.2
b = sin(IG.time()*0.1)*0.4+0.6
for i in range(len(self.points)) :
if IRand.pct(40) : #only 40%
IG.meshSquareStick(agent.points[i],self.points[i],meshSize).clr(r,g,b)
class MyBoid(IBoid) :
def __init__(self, p, v) :
IBoid.__init__(self,p,v)
self.points = None
self.prevPoints = None
self.cohesionDist(60)
self.cohesionRatio(5)
self.separationDist(50)
self.separationRatio(8)
self.alignmentDist(40)
self.alignmentRatio(0)
def update(self) : #drawing line
if self.time()%2==0 : #adjusting interval
pointNum = 3
self.points = []
radius = sin(IG.time()*0.1)*2 + 3 #changing radius by time
for i in range(pointNum) :
axis = self.vel().cross(IG.zaxis)
axis.len(radius)
axis.rot(self.vel(), 2*PI/pointNum*i)
self.points.append(self.pos().cp(axis))
Anchor(self) #leaving an anchor behind
meshSize = 0.5
r = sin(IG.time()*0.1)*0.1+0.3
g = 0.2
b = sin(IG.time()*0.1)*0.4+0.6
if self.prevPoints is not None :
for i in range(pointNum) :
IG.meshSquareStick(self.points[i], self.prevPoints[i], meshSize).clr(r,g,b)
IG.meshSquareStick(self.points[i], self.prevPoints[(i+1)%pointNum], meshSize).clr(r,g,b)
IG.meshSquareStick(self.points[i], self.points[(i+1)%pointNum], meshSize).clr(r,g,b)
self.prevPoints = self.points
class Attractor(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p) :
self.pos = p
def interact(self, agents) :
attraction = 0.4
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyBoid) :
frc = agent.pos().dif(self.pos).mul(attraction)
agent.pull(frc)
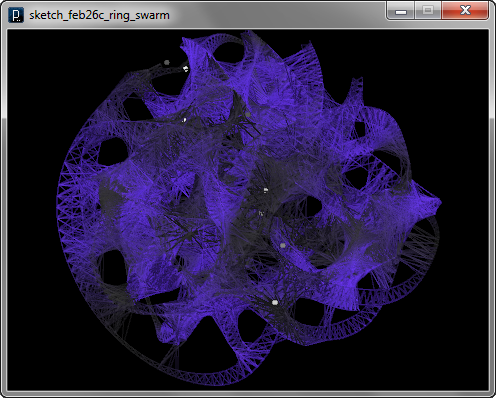


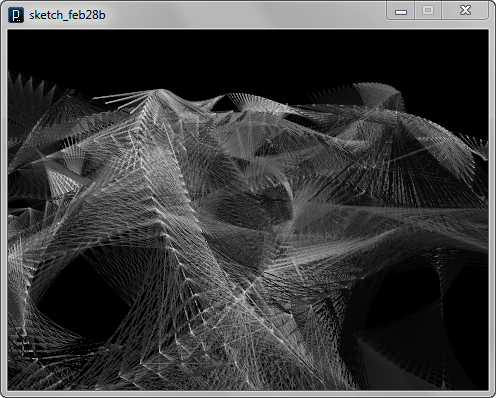
The image below shows rendered geometries.

 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
