

 Python Tutorials Python Tutorials | (back to the list of tutorials) |
 Reproduction Based Agent
Reproduction Based AgentOn the other hand, a particle based agent moves by itself. The movement follows the physical rules in Newton's law as described on the tutorial page about particles. Particles move around following forces applied to them. The result of the system are created as trajectories or some geometries built on the course of particle movement and their interaction.
This page shows examples to build a custom reproduction based agent. As the starting point, the following code defines a simple reproduction based agent with two point properties with IVec variables. The update method creates one line with the two points as geometry representation of an agent. It also contains a rule to reproduce one child agent in the same direction at the end point of the parent agent.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
MyAgent(IG.v(), IG.v(0,1,0))
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0) #geometry representation
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir) #reproduce

 Transformation Rule in Update Method
Transformation Rule in Update Method![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
MyAgent(IG.v(), IG.v(0,1,0))
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0) #geometry representation
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir.rot(PI/100) # transformation rule 1: rotate
dir.mul(0.999) # transformation rule 2: scale down
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir) #reproduce

 Branching Rule in Update Method
Branching Rule in Update Method![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
MyAgent(IG.v(), IG.v(0,1,0))
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0) #geometry representation
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir.rot(PI/100) # transformation rule 1: rotate
dir.mul(0.999) # transformation rule 2: scale down
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir) # branch 1
dir2 = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir2.rot(-PI/10)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir2) # branch 2
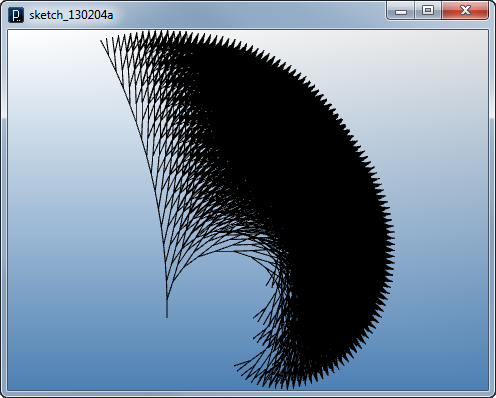
You can see that the result shows too many agents and if you run the code it gets very slow quickly because it generates exponential number of agents every time frame. This means creating two agents every time frame is too much. There are many ways to control number of child agents. The following code is one example to control branching by random number. It creates the second child agent only in 3% probability.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
MyAgent(IG.v(), IG.v(0,1,0))
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0) #geometry representation
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir.rot(PI/100) # transformation rule 1: rotate
dir.mul(0.999) # transformation rule 2: scale down
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir) # branch 1
if IRand.pct(3) : # 3% probability
dir2 = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir2.rot(-PI/10)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir2) # branch 2
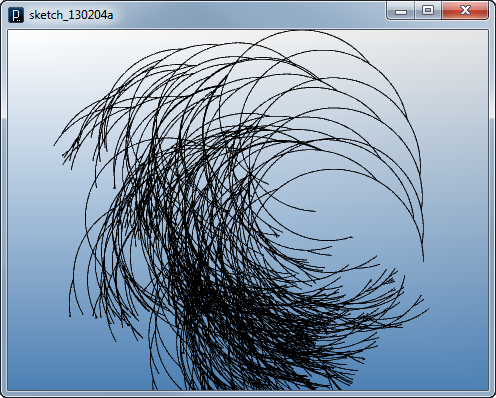
 Collision Detection Rule in Interact Method
Collision Detection Rule in Interact Method!intxn.eq(pt1) // intersection and pt1 are not at the same location
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
MyAgent(IG.v(), IG.v(0,1,0))
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time()==0 :
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyAgent) :
if agent is not self :
intxn = IVec.intersectSegment(agent.pt1,agent.pt2,self.pt1,self.pt2)
if intxn is not None and not intxn.eq(self.pt1) :
self.del()
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0) #geometry representation
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir.rot(PI/100) # transformation rule 1: rotate
dir.mul(0.999) # transformation rule 2: scale down
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir) # branch 1
if IRand.pct(3) : # 3% probability
dir2 = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir2.rot(-PI/10)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir2) # branch 2
 Adding A Property to Agent 1
Adding A Property to Agent 1boolean isStraight;
The constructor of MyAgent class adds another input argument of boolean variable straight as the line below.
MyAgent(IVec pt, IVec dir, boolean straight){
Then the new agent instance property of isStraight is initialized by this input argument straight. In the update method, this property is used to differentiate the agent behavior. When isStraight is true, it doesn't apply the transformation rule to bend the direction and it only creates one child agent. If false, it applys the original behavior to the agent with the transformation rule and the branching rule. This property isStraight is passed through the child agents as well to keep the state. The update method contains another rule to toggle this boolean state randomly in low probability as the following line.
if(IRand.pct(0.8)){ isStraight = !isStraight; } // toggle boolean switch
Then isStraight is fed to child agents to pass the current state of the parent agent.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
MyAgent(IG.v(), IG.v(0,1,0), True)
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir, straight) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isStraight = straight
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time()==0 :
for agent in agents :
if not self.alive() :
return
if isinstance(agent, MyAgent) :
if agent is not self :
intxn = IVec.intersectSegment(agent.pt1,agent.pt2,self.pt1,self.pt2)
if intxn is not None and not intxn.eq(self.pt1) :
self.del()
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0) #geometry representation
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
if IRand.pct(0.8) :
self.isStraight = not self.isStraight #toggle boolean switch
if self.isStraight :
MyAgent(self.pt2,dir,self.isStraight)
else :
dir.rot(PI/100)
dir.mul(0.999)
MyAgent(self.pt2,dir,self.isStraight)
if IRand.pct(3) :
dir2 = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir2.rot(-PI/10)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir2, self.isStraight)

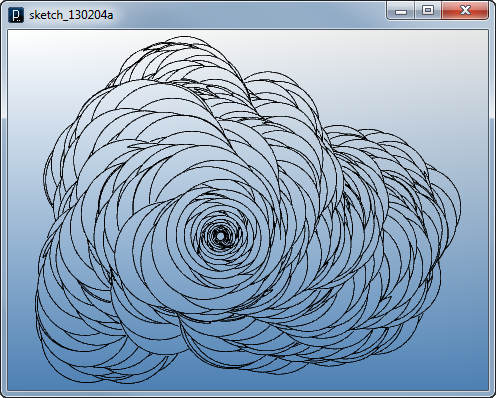
 Adding A Property to Agent 2
Adding A Property to Agent 2double angle;
The example codes above so far had a constant number for the bending angle. Now introducing the angle property makes it possible to change the bending angle gradiently through branching and propagation of agents. Inside the update method, the angle is sometimes randomly increased or decreased and also flipped to positive or negative number to flip the bending direction.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
MyAgent(IG.v(), IG.v(0,1,0), True, 0)
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir, straight, ang) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isStraight = straight
self.angle = ang
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time()==0 :
for agent in agents :
if not self.alive() :
return
if isinstance(agent, MyAgent) :
if agent is not self :
intxn = IVec.intersectSegment(agent.pt1,agent.pt2,self.pt1,self.pt2)
if intxn is not None and not intxn.eq(self.pt1) :
self.del()
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0)
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
if IRand.pct(0.8) :
self.isStraight = not self.isStraight
if self.isStraight :
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir, self.isStraight, self.angle)
else :
dir.rot(self.angle)
dir.mul(0.999)
if IRand.pct(1) :
self.angle += IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
self.angle = -self.angle # flip bending direction
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir, self.isStraight, self.angle)
if IRand.pct(3) :
dir2 = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir2.rot(-PI/10)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir2, self.isStraight, self.angle)
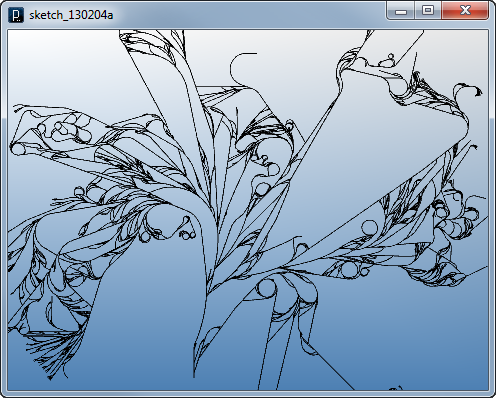
 Other Agent Classes to Interact 1
Other Agent Classes to Interact 1![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
MyAgent(IG.v(), IG.v(0,1,0), True, 0)
for i in range(10) :
Attractor(IRand.pt(-200,200,200,400)).clr(1.0,0,0)
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir, straight, ang) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isStraight = straight
self.angle = ang
self.target = None
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time()==0 :
minDist = -1
for agent in agents :
if not self.alive() :
return
if isinstance(agent, MyAgent) :
if agent is not self :
intxn = IVec.intersectSegment(agent.pt1,agent.pt2,self.pt1,self.pt2)
if intxn is not None and not intxn.eq(self.pt1) :
self.del()
elif isinstance(agent, Attractor) :
# find the closest attractor in front
dist = agent.pos.dist(self.pt2)
if minDist < 0 : # first time to check Attractor
minDist = dist
self.target = agent
elif dist < minDist :
minDist = dist
self.target = agent
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(0)
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
if IRand.pct(0.8) :
self.isStraight = not self.isStraight
if self.isStraight :
if self.target is not None :
targetDir = self.target.pos.dif(self.pt2)
if dir.cp().rot(self.angle).angle(targetDir) > \
dir.cp().rot(-self.angle).angle(targetDir) :
self.angle = -self.angle # angle closer to target
dir.rot(self.angle) # rotate toward target
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir, self.isStraight, self.angle) # branch 1
else :
if IRand.pct(1) :
self.angle += IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
self.angle = -self.angle
if self.target is not None :
targetDir = self.target.pos.dif(self.pt2)
if dir.cp().rot(self.angle).angle(targetDir) > \
dir.cp().rot(-self.angle).angle(targetDir) :
self.angle = -self.angle # angle closer to target
dir.rot(self.angle) # rotate toward target
dir.mul(0.999)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir, self.isStraight, self.angle) # branch 1
else :
dir.rot(self.angle)
dir.mul(0.999)
if IRand.pct(99) :
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir, self.isStraight, self.angle) # branch 1
if IRand.pct(3) : # 3% probability
dir2 = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir2.rot(-PI/10)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir2, self.isStraight, self.angle) # branch 2
class Attractor(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p) :
self.pos = p
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
IPoint(self.pos).clr(self.clr())
 Other Agent Classes to Interact 2
Other Agent Classes to Interact 2![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
add_library('igeo')
def setup() :
size(480, 360, IG.GL)
IG.open("agent_lines1.3dm") # input file to initialize agents
roots = IG.layer("root").curves()
bounds = IG.layer("boundary").curves()
attractors = IG.layer("attractor").points()
for crv in roots :
MyAgent(crv.start(), crv.end().dif(crv.start()), 0)
for pt in attractors :
Attractor(pt.pos()).clr(IRand.clr())
pt.del()
for crv in bounds :
BoundaryAgent(crv)
IG.bg(0)
class MyAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, pt, dir, ang) :
self.pt1 = pt
self.pt2 = pt.cp(dir)
self.isStraight = True
self.angle = ang
self.target = None
def interact(self, agents) :
if self.time()==0 :
minDist = -1
for agent in agents :
if not self.alive() :
return
if isinstance(agent, MyAgent) :
if agent is not self :
intxn = IVec.intersectSegment(agent.pt1,agent.pt2,self.pt1,self.pt2)
if intxn is not None and not intxn.eq(self.pt1) :
self.del()
elif isinstance(agent, Attractor) :
# find the closest attractor in front
dist = agent.pos.dist(self.pt2)
if minDist < 0 : # first time to check Attractor
minDist = dist
self.target = agent
elif dist < minDist :
minDist = dist
self.target = agent
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
ICurve(self.pt1, self.pt2).clr(self.clr().cp())
dir = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
if self.isStraight : # just go straight
if self.target is not None :
self.clr().blend(self.target.clr(),0.02) # blend 2% color
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir, self.angle).clr(self.clr().cp()) # branch 1
else :
if IRand.pct(1) :
self.angle += IRand.get(-0.05, 0.05)
self.angle = -self.angle
if self.target is not None :
targetDir = self.target.pos.dif(self.pt2)
if dir.cp().rot(self.angle).angle(targetDir) > \
dir.cp().rot(-self.angle).angle(targetDir) :
self.angle = -self.angle # angle closer to target
dir.rot(self.angle) # rotate toward target
dir.mul(0.999)
self.clr().blend(self.target.clr(),0.02) # blend 2% color
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir, self.angle).clr(self.clr().cp()) # branch 1
else :
dir.rot(self.angle)
dir.mul(0.999)
if IRand.pct(100) :
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir, self.angle).clr(self.clr().cp()) # branch 1
if IRand.pct(3) : # 3% probability
dir2 = self.pt2.dif(self.pt1)
dir2.rot(-PI/10)
MyAgent(self.pt2, dir2, self.angle).clr(self.clr().cp()) # branch 2
class Attractor(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, p) :
self.pos = p
def update(self) :
if self.time()==0 :
IPoint(self.pos).clr(self.clr())
class BoundaryAgent(IAgent) :
def __init__(self, crv) :
self.boundary = crv
def interact(self, agents) :
for agent in agents :
if isinstance(agent, MyAgent) :
if agent.time()==0 : # check only what's just created
if self.boundary.isInside2d(agent.pt2) : # check if it's inside
agent.isStraight=False

 HOME
HOME
 FOR PROCESSING
FOR PROCESSING
 DOWNLOAD
DOWNLOAD
 DOCUMENTS
DOCUMENTS
 TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
TUTORIALS (Java /
Python)
 GALLERY
GALLERY
 SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
SOURCE CODE(GitHub)
 PRIVACY POLICY
PRIVACY POLICY
 ABOUT/CONTACT
ABOUT/CONTACT
