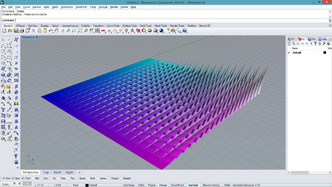
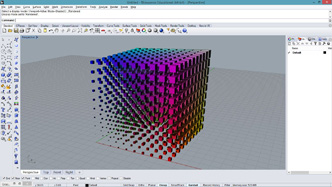
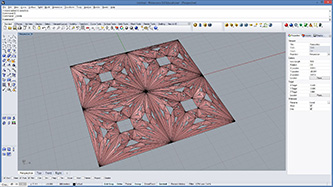
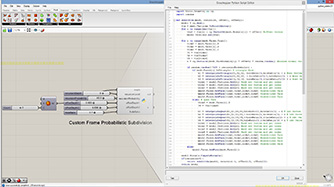
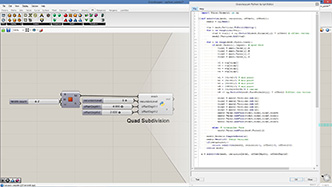
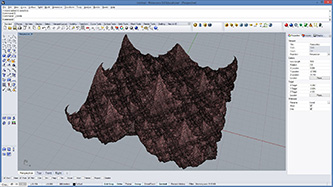
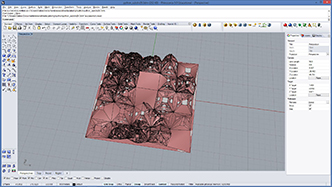
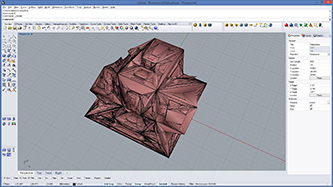
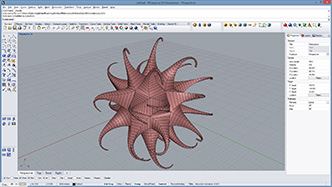
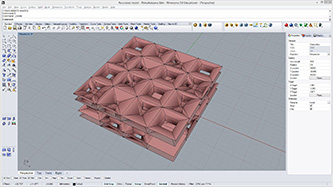
|
|
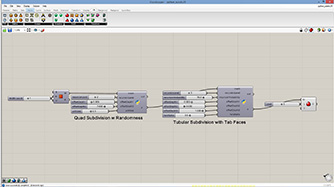
Grasshopper Python |
- RhinoPython 101 Primer
http://www.rhino3d.com/download/IronPython/5.0/RhinoPython101
- RhinoPython Reference
http://4.rhino3d.com/5/ironpython/
(In Rhinoceros menu) Tools > PythonScript > Edit
(In Rhino Python Editor menu) Help > Python Help
- RhinoCommon Reference
http://4.rhino3d.com/5/rhinocommon/
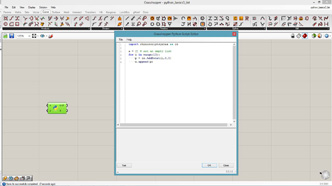
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs text = "hello world" print text # comment a = rs.AddPoint(0,0,0)
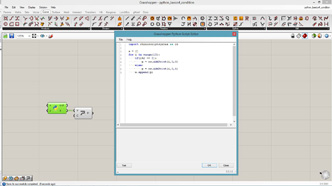
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
for i in range(10):
print(i)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
a = [] # set an empty list
for i in range(10):
p = rs.AddPoint(i,0,0)
a.append(p)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
a = []
for i in range(10):
if(i%2 == 0):
p = rs.AddPoint(i,0,0)
else:
p = rs.AddPoint(i,0,5)
a.append(p)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
a = []
for i in range(10):
if(i < 5):
p = rs.AddPoint(i,0,0)
elif(i < 8):
p = rs.AddPoint(i,0,6)
else:
p = rs.AddPoint(i,0,2)
a.append(p)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import math
a = []
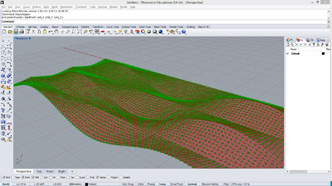
for i in range(500):
x = math.cos(i*0.1) * i*0.1
y = math.sin(i*0.1) * i*0.08
if(i < 200):
z = i*0.05
else:
z = 20-i*0.05
p = rs.AddPoint(x,y,z)
a.append(p)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import random
import math
a = []
for i in range(500):
x = math.cos(i*0.2) * i*0.1
y = math.sin(i*0.2) * i*0.08
if(i<200):
z = 0
else:
z = random.random() * (i-200)* 0.02
p = rs.AddPoint(x,y,z)
a.append(p)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import math
a = []
for i in range(100):
for j in range(50):
x = i*0.5
y = j*0.5
z = math.sin(i*0.1)*1;
if(j%20 < 10):
z *= (j%20)*0.2;
else:
z *= (20 - j%20)*0.2;
p = rs.AddPoint(x,y,z)
a.append(p)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import math
a = []
for i in range(100):
for j in range(100):
x = i*0.5
y = j*0.5
if( i<20 and j<20 ):
z = 2
elif( i>=20 and i<40 and j>=60 and j<80):
z = 1
elif( i==50 or j==50):
z = 2
elif( i>=60 and i<80 and j>=20 and j<80):
z = math.cos(j*0.2)+2
elif( not i>60 and j>=25 and j<35):
z = 8 - i*0.1
elif( not (i<90 and j<90) ):
z = math.sin(i*0.2) * math.cos(j*0.2)+2
else:
z = math.cos(i*0.1) * math.sin(j*0.1)
p = rs.AddPoint(x,y,z)
a.append(p)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import math
a = []
for i in range(100):
for j in range(100):
x = i*0.5
y = j*0.5
if( i%20<4 or j%20<4 ):
z = 0
elif( i%20+j%20 > 20):
z = ((20 - i%20) * (j%20))*0.03
z += math.cos(i*0.1) * math.sin(j*0.1)*2+2
elif( i%20>=5 and j%20<10 ):
z = ((i%20)*(i%20)/20 + (j%20)/2)*0.3
else:
z = ((i%20)*0.2 + (j%20)*0.3)
p = rs.AddPoint(x,y,z)
a.append(p)
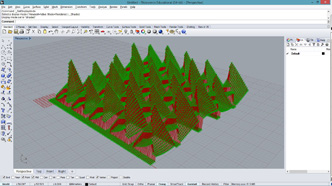
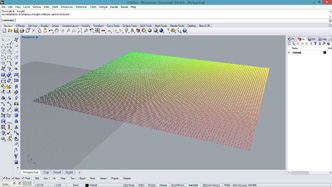
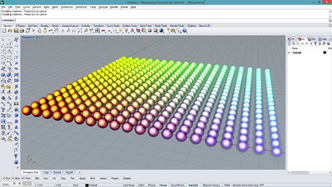
#building a point grid out of input parameters
#input type - x : int, y : int, z : float, u : float
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import math
a = []
for i in range(x):
for j in range(y):
p = rs.AddPoint(i, j, math.sin(i*u) * math.sin(j*u) * z)
a.append(p)
# separate input points into 3 output groups
# input type - x : Point3d (ListAccess)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import math
a = []
b = []
c = []
for pt in x:
if(pt.X % 3 < 0.5):
a.append(pt)
elif( math.sqrt(pt.Y) %0.5 < 0.1):
b.append(pt)
else:
c.append(pt)
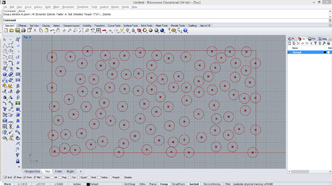
# This separates points and creates attractor controlled circles or rectangles
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), attr : Point3d (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg # Geometry library
import math
a = []
b = []
for pt in pts:
if( pt.Y % 10 > 0 and pt.Y % 10 < 2):
rect = rs.AddRectangle(rg.Plane.WorldXY, 1.5, 0.4)
rs.MoveObject(rect, pt)
rs.MoveObject(rect, rg.Vector3d(-0.75,-0.2,0))
a.append(rect)
else:
dist = rs.Distance(pt, attr)
circle = rs.AddCircle(pt, 0.02*dist)
b.append(circle)
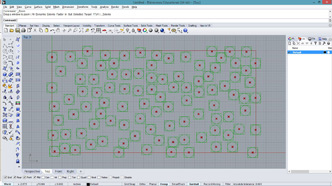
# This connects points within the input distance only if number of connection is more than a certain number
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
a = []
for pt in pts:
closePts = []
for pt2 in pts:
dist = rs.Distance(pt, pt2)
if(dist > 0 and dist < threshold): # exclude itself by > 0
closePts.append(pt2)
count = len(closePts)
if(count >= 3):
for cpt in closePts:
zpt = rs.AddPoint(pt.X, pt.Y, 0.5*(count-2))
line = rs.AddLine(zpt, cpt)
a.append(line)
# draw lines between closest points on the input curves
# input type - curves : Curve (List Access), div : int
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
a = []
b = []
for crv1 in curves:
for i in range(div+1):
pt1 = crv1.PointAt(i/div)
a.append(pt1)
minDist = -1 #initialize
for crv2 in curves:
if(crv1 != crv2):
for j in range(div+1):
pt2 = crv2.PointAt(j/div)
dist = rs.Distance(pt1, pt2)
if(minDist < 0): # first time to check
closest = pt2
minDist = dist
elif(dist < minDist):
closest = pt2
minDist = dist
line = rs.AddLine(pt1, closest)
b.append(line)
# this takes intersection of all curves and build geometry around the intersection
# input type - curves : Curve (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
a = []
b = []
for curve1 in curves:
for curve2 in curves:
if( curve1 != curve2):
itxn = rg.Intersect.Intersection.CurveCurve(curve1, curve2, 0.0001, 0.0001)
for item in itxn.Item:
# intersection point
ipt = item.PointA
a.append(ipt)
# build geometry at intersection
[success, t] = curve1.ClosestPoint(ipt) # get t parameter
if(success):
tan = curve1.TangentAt(t) # get tangent vector
tan *= 2
pt1 = rg.Point3d(ipt) # copy a new point
pt1 += tan
pt2 = rg.Point3d(ipt)
pt2 -= tan
pt3 = rg.Point3d(ipt)
pt3 += rg.Vector3d(0,0,10)
surf = rs.AddSrfPt([pt1, pt2, pt3])
b.append(surf)
# This makes surface panels by 4 points on an input surface
# input type - surf : Surface, unum : int, vnum : int
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
panels = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
pt11 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
pt12 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, j/vnum)
pt21 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt22 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt11, pt12, pt22, pt21)
panels.append(panel)
# This makes surface panels by 3 points on an input surface
# input type - surf : Surface, unum : int, vnum : int
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
panels = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
pt1 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
pt2 = surf.PointAt((i+0.9)/unum, (j+0.1)/vnum)
pt3 = surf.PointAt((i+1.2)/unum, (j+1.0)/vnum)
pt4 = surf.PointAt((i+0.3)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt5 = surf.PointAt((i+0.6)/unum, (j+0.3)/vnum)
n1 = surf.NormalAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
n2 = surf.NormalAt((i+0.9)/unum, (j+0.1)/vnum)
n3 = surf.NormalAt((i+1.2)/unum, (j+1.0)/vnum)
n4 = surf.NormalAt((i+0.3)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
n5 = surf.NormalAt((i+0.6)/unum, (j+0.3)/vnum)
pt1 += n1*0.2
pt2 += n2*0.2
pt3 += n3*-0.1
pt4 += n4*1.3
pt5 += n5*1.5
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt2, pt3, pt5)
panels.append(panel)
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt3, pt4, pt5)
panels.append(panel)
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt4, pt1, pt5)
panels.append(panel)
# This makes surface panels by lofting on an input surface
# input type - surf : Surface, unum : int, vnum : int, panelWdith : float, panelDepth : float
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
panels = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
pt11 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
pt12 = surf.PointAt((i+panelWidth)/unum, j/vnum)
pt21 = surf.PointAt((i+0.5)/unum, (j+0.75)/vnum)
pt22 = surf.PointAt((i+0.5+panelWidth)/unum, (j+0.75)/vnum)
pt31 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1.5)/vnum)
pt32 = surf.PointAt((i+1+panelWidth)/unum, (j+1.5)/vnum)
n21 = surf.NormalAt((i+0.25)/unum, (j+0.5)/vnum)
n22 = surf.NormalAt((i+0.25+panelWidth)/unum, (j+0.5)/vnum)
pt21 += n21*panelDepth
pt22 += n22*panelDepth
line1 = rg.LineCurve(pt11, pt12)
line2 = rg.LineCurve(pt21, pt22)
line3 = rg.LineCurve(pt31, pt32)
panelSurf = rg.Brep.CreateFromLoft([line1, line2, line3], rg.Point3d.Unset, rg.Point3d.Unset, rg.LoftType.Straight, False)
panels.extend(panelSurf)
# This makes surface panels by 6 points on an input surface
# input type: surf - Surface, unum - int, vnum - int, panelDepth - float
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
panels = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
if j % 4 == 0:
pt11 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, j/vnum)
pt21 = surf.PointAt((i+1.5+math.sin((i+1)*0.5)*0.5)/unum, j/vnum)
pt31 = surf.PointAt((i+2)/unum, j/vnum)
pt12 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt22 = surf.PointAt((i+0.5+math.sin(i*0.5)*0.5)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt32 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
n21 = surf.NormalAt((i+1.5+math.sin((i+1)*0.5)*0.5)/unum, j/vnum)
n22 = surf.NormalAt((i+0.5+math.sin(i*0.5)*0.5)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt21 += n21*panelDepth * math.sin(j*0.4)
pt22 += n22*panelDepth * math.sin((j+1)*0.4)
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt11,pt21,pt22,pt12)
panels.append(panel)
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt21,pt31,pt32,pt22)
panels.append(panel)
else:
pt11 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
pt21 = surf.PointAt((i+0.5+math.sin(i*0.5)*0.5)/unum, j/vnum)
pt31 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, j/vnum)
pt12 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt22 = surf.PointAt((i+1.5+math.sin((i+1)*0.5)*0.5)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt32 = surf.PointAt((i+2)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
n21 = surf.NormalAt((i+0.5+math.sin(i*0.5)*0.5)/unum, j/vnum)
n22 = surf.NormalAt((i+1.5+math.sin((i+1)*0.5)*0.5)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt21 += n21*panelDepth * math.sin(j*0.4)
pt22 += n22*panelDepth * math.sin((j+1)*0.4)
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt11,pt21,pt22,pt12)
panels.append(panel)
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt21,pt31,pt32,pt22)
panels.append(panel)
# This makes surface panels by 6 points on an input surface
# input type: surf - Surface, unum - int, vnum - int, panelDepth - float
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
panels = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
ratio = (i+j)%6 / 6
pt11 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
pt21 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, j/vnum)
pt12 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, (j+0.5)/vnum)
pt22 = surf.PointAt((i+1+ratio)/unum, (j+0.5)/vnum)
pt13 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt23 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
n22 = surf.NormalAt((i+1)/unum, (j+0.5)/vnum)
pt22 += n22* panelDepth * ratio
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt11,pt21,pt22,pt12)
panels.append(panel)
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt12,pt22,pt23,pt13)
panels.append(panel)
# This makes surface panels by lofting on an input surface
# input type: surf - Surface, unum - int, vnum - int, panelDepth - float
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
panels = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
pt1 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
pt2 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, j/vnum)
pt3 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
pt4 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
if random.random() < 0.7:
n1 = surf.NormalAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
n2 = surf.NormalAt((i+1)/unum, j/vnum)
n3 = surf.NormalAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
n4 = surf.NormalAt(i/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
uvRatio = random.random()*0.3
depthRatio = random.random()
pt5 = surf.PointAt((i+0.5-uvRatio)/unum, (j+0.5-uvRatio)/vnum)
pt6 = pt2
pt7 = surf.PointAt((i+0.5+uvRatio)/unum, (j+0.5+uvRatio)/vnum)
pt8 = pt4
pt5 += n1 * panelDepth * depthRatio
pt6 += n2 * panelDepth * depthRatio * 0.5
pt7 += n3 * panelDepth * depthRatio
pt8 += n4 * panelDepth * depthRatio * 0.5
polyline1 = rg.PolylineCurve([pt1,pt2,pt3,pt4,pt1])
polyline2 = rg.PolylineCurve([pt5,pt6,pt7,pt8,pt5])
panelSurf = rg.Brep.CreateFromLoft([polyline1, polyline2], rg.Point3d.Unset, rg.Point3d.Unset, rg.LoftType.Straight, False)
panels.extend(panelSurf)
else:
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt1, pt2, pt3, pt4)
panels.append(panel)
# this iterates a tree of points and put circles
# input type - ptTree : Point3d (Tree Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
a = []
for ptList in ptTree.Branches:
for pt in ptList:
circle = rs.AddCircle(pt, 0.4)
a.append(circle)
# this iterates a tree of points and put circles
# input type - ptTree : Point3d (Tree Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
a = []
for i in range(ptTree.BranchCount):
ptList = ptTree.Branch(i)
ptNum = len(ptList)
for j in range(ptNum):
if( i==10 and j==23 or i==20 and j==2 or i==32 and j==18):
circle = rs.AddCircle(ptList[j], 1)
else:
circle = rs.AddCircle(ptList[j], 0.2)
a.append(circle)
# this connects closest points between branches in a tree
# input type - ptTree : Curve (Tree Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
a = []
for ptList in ptTree.Branches:
for pt in ptList:
minDist = -1 # initialize
for ptList2 in ptTree.Branches:
if(ptList!=ptList2):
print len(ptList2)
for pt2 in ptList2:
dist = rs.Distance(pt, pt2)
if(minDist < 0): # first time
minDist = dist
closest = pt2
elif(dist < minDist):
minDist = dist
closest = pt2
line = rs.AddLine(pt, closest)
a.append(line)
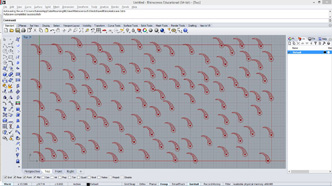
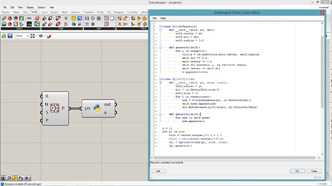
# This draws a line pattern at each input point
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
# function definition
def drawWhorl(pt):
r1 = 0.3
r2 = 1
num = 30
lines = []
for i in range(num):
vec1 = rg.Vector3d(r1, 0, 0)
vec1.Rotate(math.pi*2*i/num + math.pi/3, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
vec2 = rg.Vector3d(r2, 0, 0)
vec2.Rotate(math.pi*2*i/num, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
vec1 += pt
vec2 += pt
line = rs.AddLine(vec1, vec2)
lines.append(line)
return lines
# main
a = []
for pt in pts:
lines = drawWhorl(pt)
a.extend(lines) # add all lines
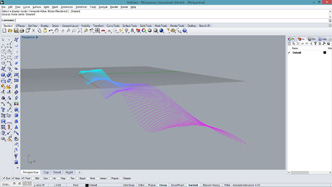
# this adds tubular surface on an input surface by a function
# input type - surf : Surface (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def addTube(pt, normal, radius):
circle1 = rs.AddCircle(rg.Plane(pt, normal), radius)
pt2 = pt + normal * 0.1
circle2 = rs.AddCircle(rg.Plane(pt2, normal), radius*0.5)
pt3 = pt + normal * 0.5
circle3 = rs.AddCircle(rg.Plane(pt3, normal), radius*0.2)
loftResult = rs.AddLoftSrf([circle1, circle2, circle3])
return loftResult # loftResult is a list
a = []
vshift = 0
for i in range(1, udiv):
vshift += 0.01
for j in range(vdiv):
u = i/udiv
v = j/vdiv + vshift
if(v > 1.0): v = v%1.0
pt = surf.PointAt(u,v)
nml = surf.NormalAt(u,v)
result = addTube(pt, nml, 0.6-u*0.5)
a.extend(result) # result is a list
# This adds curves on the input curve rotated from tis tangent direction
# input type - curve : Curve (Item Access), count : int (Item Access), axis : Vector3d (Item Access), angle : float (Item Access), length : float (Item Access), frequency : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def curveOnCurve(crv, u, length, angle, axis, rollAngle):
pt = crv.PointAt(u)
tan = crv.TangentAt(u)
ax = rg.Vector3d(axis)
ax.Rotate(rollAngle, tan)
tan.Rotate(angle, ax)
tan.Unitize()
pt2 = pt + tan * length
tan.Rotate(angle, axis)
pt3 = pt2 + tan * length
return rg.NurbsCurve.Create(False, 2, [pt, pt2, pt3])
a = []
for i in range(count+1):
u = i/count
ang = angle/180*math.pi + math.sin(frequency*u*math.pi)*0.5
len = length * (math.cos(frequency*u*math.pi)+1)/2
crv = curveOnCurve(curve, u, len, ang, axis, u*math.pi)
a.append(crv)
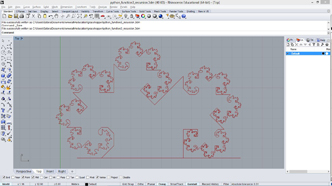
# this creates fractal lines by recursive function
# input type - line : Line (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def recursiveLine(line, depth, resultList):
pt1 = line.PointAt(0)
pt2 = line.PointAt(0.15)
pt3 = line.PointAt(0.65)
pt4 = line.PointAt(0.65)
pt5 = line.PointAt(1.0)
dir = rg.Vector3d(pt5.X-pt1.X, pt5.Y-pt1.Y, pt5.Z-pt5.Z)
dir.Rotate(math.pi/2, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
pt3 += dir * 0.5
line1 = rg.Line(pt1, pt2)
line2 = rg.Line(pt2, pt3)
line3 = rg.Line(pt3, pt4)
line4 = rg.Line(pt4, pt5)
resultList.append(line1)
resultList.append(line4)
if(depth>0):
recursiveLine(line2, depth-1, resultList) # recursion
recursiveLine(line3, depth-1, resultList) # recursion
else:
resultList.append(line2)
resultList.append(line3)
# main
a = []
recursiveLine(line, 9, a)
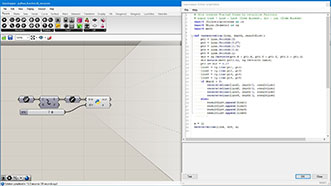
# this creates fractal lines by recursive function
# input type - line : Line (Item Access), div : int (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def recursiveLine(line, depth, resultList):
pt1 = line.PointAt(0)
pt2 = line.PointAt(0.27)
pt3 = line.PointAt(0.75)
pt4 = line.PointAt(0.6)
pt5 = line.PointAt(1)
dir = rg.Vector3d(pt5.X - pt1.X, pt5.Y - pt1.Y, pt5.Z - pt1.Z)
dir.Rotate(math.pi*0.42, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
pt3 += dir * 0.27
line1 = rg.Line(pt1, pt2)
line2 = rg.Line(pt2, pt3)
line3 = rg.Line(pt3, pt4)
line4 = rg.Line(pt4, pt5)
if depth > 0:
recursiveLine(line1, depth-1, resultList)
recursiveLine(line2, depth-1, resultList)
recursiveLine(line3, depth-1, resultList)
recursiveLine(line4, depth-1, resultList)
else:
resultList.append(line1)
resultList.append(line2)
resultList.append(line3)
resultList.append(line4)
a = []
recursiveLine(line, div, a)
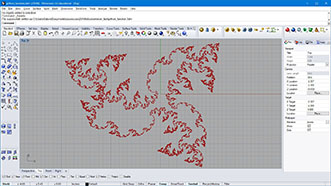
# this creates fractal lines by recursive function
# input type - line : Line (Item Access), div : int (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def recursiveLine(line, depth, axis, resultList):
pt1 = line.PointAt(0)
pt2 = line.PointAt(0.3)
pt3 = line.PointAt(0.3)
pt4 = line.PointAt(0.6)
pt5 = line.PointAt(0.6)
pt6 = line.PointAt(1)
dir = pt6 - pt1
dir2 = rg.Vector3d(dir)
dir2.Rotate(math.pi*0.5, axis)
dir2.Rotate(math.pi*0.5, dir)
pt3 += dir2 * 0.5
pt4 += dir2 * 0.5
line1 = rg.Line(pt1, pt2)
line2 = rg.Line(pt2, pt3)
line3 = rg.Line(pt3, pt4)
line4 = rg.Line(pt4, pt5)
line5 = rg.Line(pt5, pt6)
if depth > 0:
axis = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(dir, dir2)
recursiveLine(line1, depth-1, axis, resultList)
recursiveLine(line2, depth-1, axis, resultList)
recursiveLine(line3, depth-1, axis, resultList)
recursiveLine(line4, depth-1, axis, resultList)
recursiveLine(line5, depth-1, axis, resultList)
else:
resultList.append(line1)
resultList.append(line2)
resultList.append(line3)
resultList.append(line4)
resultList.append(line5)
a = []
recursiveLine(line, div, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis, a)
# this creates fractal lines and surfaces by recursive function
# input type - line : Line (Item Access), div : int (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def recursiveLine(line, depth, axis, resultList):
pt1 = line.PointAt(0)
pt2 = line.PointAt(0.1)
pt3 = line.PointAt(0.7)
pt4 = line.PointAt(0.8)
pt5 = line.PointAt(1)
dir = pt5 - pt1
dir2 = rg.Vector3d(dir) # copy
dir2.Rotate(math.pi*0.5, axis)
dir2.Rotate(math.pi*0.25, dir)
pt3 += dir2 * 0.45
line1 = rg.Line(pt1, pt2)
line2 = rg.Line(pt2, pt3)
line3 = rg.Line(pt3, pt4)
line4 = rg.Line(pt4, pt5)
srf = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt2,pt3,pt4)
resultList.append(srf)
if depth > 0:
axis = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(dir, dir2)
recursiveLine(line1, depth-1, axis, resultList)
recursiveLine(line2, depth-1, axis, resultList)
recursiveLine(line3, depth-1, axis, resultList)
recursiveLine(line4, depth-1, axis, resultList)
else:
resultList.append(line1)
resultList.append(line2)
resultList.append(line3)
resultList.append(line4)
a = []
recursiveLine(line, div, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis, a)
# this creates random branching lines with recursion
# input type - line : Line (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def recursiveLine(line, depth, resultList):
pt1 = line.PointAt(0)
pt2 = line.PointAt(1)
dir1 = rg.Vector3d(pt2.X-pt1.X, pt2.Y-pt1.Y, pt2.Z-pt1.Z)
dir2 = rg.Vector3d(dir1) # copy
dir1.Rotate(random.random()*0.4+0.1, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis) # random angle
dir2.Rotate(random.random()*-0.4-0.1, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
dir1 *= random.random()*0.2 + 0.8; # random scale
dir2 *= random.random()*0.2 + 0.8;
line1 = rg.Line(pt2, pt2+dir1)
line2 = rg.Line(pt2, pt2+dir2)
resultList.append(line1)
resultList.append(line2)
if(depth>0):
if(random.random()<0.9): # random omission
recursiveLine(line1, depth-1, resultList)
if(random.random()<0.8): # random omission
recursiveLine(line2, depth-1, resultList)
# main
a = []
recursiveLine(line, 10, a)
# this creates random branching lines with recursion
# input type: line - Line (Item Access), div - int (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
import math
def recursiveLine(line, depth, resultList):
pt1 = line.PointAt(0)
pt2 = line.PointAt(1)
dir1 = pt2 - pt1
dir2 = rg.Vector3d(dir1) # copy
dir1.Rotate(math.pi/3, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis) # random angle
dir2.Rotate(-math.pi/3, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
dir1 *= random.random()*0.2 + 0.7; # random scale
dir2 *= random.random()*0.2 + 0.7;
line1 = rg.Line(pt2, pt2+dir1)
line2 = rg.Line(pt2, pt2+dir2)
resultList.append(line1)
resultList.append(line2)
if(depth>0):
if(random.random()<0.9): # random omission
recursiveLine(line1, depth-1, resultList)
if(random.random()<0.8): # random omission
recursiveLine(line2, depth-1, resultList)
a = []
recursiveLine(line, div, a)
# Rectangular surface recursion
# input type - surf : Surface (Item Access), offset : float (Item Access), scale : float (Item Access), percent : float (Item Access), recursion : int (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def recursiveSurf(surf, offs, depth):
for i in range(2):
for j in range(2):
if random.random()*100 < percent:
pt1 = surf.PointAt(i/2, j/2)
pt2 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/2, j/2)
pt3 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/2, (j+1)/2)
pt4 = surf.PointAt(i/2, (j+1)/2)
center = (pt1+pt2+pt3+pt4)/4
pt1 = (pt1-center)*scale+center
pt2 = (pt2-center)*scale+center
pt3 = (pt3-center)*scale+center
pt4 = (pt4-center)*scale+center
n = surf.NormalAt((i+0.5)/2, (j+0.5)/2)
n.Unitize()
n *= offset * random.random()
pt1 += n
pt2 += n
pt3 += n
pt4 += n
s = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt1,pt2,pt3,pt4)
a.append(s)
if depth > 1 and random.random()*100 < percent:
s.SetDomain(0, rg.Interval(0,1))
s.SetDomain(1, rg.Interval(0,1))
recursiveSurf(s, offs/2, depth-1)
a = []
if surf is not None:
recursiveSurf(surf, offset, recursion)
# this creates random branching lines with recursion
# input type: line - Line (Item Access), div - int (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
import math
def recursiveLine(line, depth, axis, resultList):
pt1 = line.PointAt(0)
pt2 = line.PointAt(1)
dir0 = pt2 - pt1
dir1 = rg.Vector3d(dir0) # copy
dir2 = rg.Vector3d(dir0) # copy
dir1.Rotate(math.pi/2, axis)
dir1.Rotate(math.pi/2, dir0)
dir2.Rotate(-math.pi/2, axis)
dir2.Rotate(math.pi/2, dir0)
dir1 *= random.random()*0.2 + 0.7; # random scale
dir2 *= random.random()*0.2 + 0.7;
line1 = rg.Line(pt2, pt2+dir1)
line2 = rg.Line(pt2, pt2+dir2)
resultList.append(line1)
resultList.append(line2)
axis = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(dir0,dir1)
axis.Unitize()
box = rg.Box(rg.Plane.WorldXY, [pt1, pt2, pt2+dir1, pt2+dir2, pt2+axis*dir1.Length/2])
resultList.append(box)
if(depth>0):
if(random.random()<0.9): # random omission
recursiveLine(line1, depth-1, axis, resultList)
if(random.random()<0.8): # random omission
#axis = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(dir0,dir2)
recursiveLine(line2, depth-1, axis, resultList)
a = []
recursiveLine(line, div, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis, a)
# this generates subdivided boxes on a surface recursively
# input type - surf : Surface (Item Access), unum : int (Item Access), vnum : int (Item Access), offset : float (Item Access), recursion : float (Item Access), percent : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def interpolate(pt1, pt2, ratio):
return pt1*(1-ratio) + pt2*ratio
def boxPt(pts, u, v, w):
upt11 = interpolate(pts[1][0][0], pts[0][0][0], u)
upt21 = interpolate(pts[1][1][0], pts[0][1][0], u)
upt12 = interpolate(pts[1][0][1], pts[0][0][1], u)
upt22 = interpolate(pts[1][1][1], pts[0][1][1], u)
vpt1 = interpolate(upt21,upt11, v)
vpt2 = interpolate(upt22,upt12, v)
return interpolate(vpt2,vpt1,w)
def divideBox(pts, depth):
pts2 = []
for i in range(2):
for j in range(2):
for k in range(2):
if random.random()*100 <= percent:
p111 = boxPt(pts, i/2, j/2, k/2)
p112 = boxPt(pts, i/2, j/2, (k+1)/2)
p121 = boxPt(pts, i/2, (j+1)/2, k/2)
p122 = boxPt(pts, i/2, (j+1)/2, (k+1)/2)
p211 = boxPt(pts, (i+1)/2, j/2, k/2)
p212 = boxPt(pts, (i+1)/2, j/2, (k+1)/2)
p221 = boxPt(pts, (i+1)/2, (j+1)/2, k/2)
p222 = boxPt(pts, (i+1)/2, (j+1)/2, (k+1)/2)
bpts = [[[p111,p112],[p121,p122]],[[p211,p212],[p221,p222]]]
if depth > 1 and random.random()*100 <= percent:
bpts2 = divideBox(bpts, depth-1)
pts2.extend(bpts2)
else:
pts2.append(bpts)
return pts2
a = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
p11 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
p12 = surf.PointAt(i/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
p21 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, j/vnum)
p22 = surf.PointAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
n11 = surf.NormalAt(i/unum, j/vnum)
n12 = surf.NormalAt(i/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
n21 = surf.NormalAt((i+1)/unum, j/vnum)
n22 = surf.NormalAt((i+1)/unum, (j+1)/vnum)
n11.Unitize()
n12.Unitize()
n21.Unitize()
n22.Unitize()
q11 = p11 + n11*offset
q12 = p12 + n12*offset
q21 = p21 + n21*offset
q22 = p22 + n22*offset
boxPts = divideBox([[[p11,q11],[p12,q12]],[[p21,q21],[p22,q22]]], recursion)
for b in boxPts:
box = rg.Brep.CreateFromBox([b[0][0][0],b[1][0][0],b[1][1][0],b[0][1][0],b[0][0][1],b[1][0][1],b[1][1][1],b[0][1][1]])
a.append(box)
# Hexagonal recursive branches
# input type - hexPolyline : Polyline (Item Access), length : float (Item Access), scale : float (Item Access), shift : float (Item Access), percent : float (Item Access), recursion : int (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def calcCenter(pts):
cnt = rg.Point3d(0,0,0)
for p in pts:
cnt += p
return cnt / len(pts)
def createHex(center, hpt1, hpt2, hpt3, normal):
p1 = (hpt1 + hpt2)/2
p2 = hpt2
p3 = (hpt2+hpt3)/2
p4 = (hpt3 + center)/2
p5 = center
p6 = (hpt1 + center)/2
shiftvec = (p2 - p5) * shift
q1 = p1 + normal + shiftvec
q2 = p2 + normal + shiftvec
q3 = p3 + normal + shiftvec
q4 = p4 + normal + shiftvec
q5 = p5 + normal + shiftvec
q6 = p6 + normal + shiftvec
cnt = calcCenter([q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q6])
q1 = (q1-cnt)*scale + cnt
q2 = (q2-cnt)*scale + cnt
q3 = (q3-cnt)*scale + cnt
q4 = (q4-cnt)*scale + cnt
q5 = (q5-cnt)*scale + cnt
q6 = (q6-cnt)*scale + cnt
cap1 = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(cnt, q1, q2, q3)
cap2 = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(cnt, q3, q4, q5)
cap3 = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(cnt, q5, q6, q1)
capsurf.append(cap1)
capsurf.append(cap2)
capsurf.append(cap3)
side = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromPoints([p1,p2,p3,p4,p5,p6,p1, q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q6,q1], 2, 7, 1, 1)
sidesurf.append(side)
return rg.Polyline([q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q6,q1])
def recursiveHex(hex, offset, depth):
center = calcCenter([hex[0],hex[1],hex[2],hex[3],hex[4],hex[5]])
nml = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(hex[2]-hex[0], hex[4]-hex[2])
nml.Unitize()
nml *= offset
for i in range(3):
if random.random()*100 < percent:
hpt1 = hex[i*2]
hpt2 = hex[(i*2+1)%6]
hpt3 = hex[(i*2+2)%6]
hex2 = createHex(center, hpt1, hpt2, hpt3, nml)
if depth > 1:
recursiveHex(hex2, offset*scale, depth-1)
sidesurf = []
capsurf = []
if hexPolyline is not None and hexPolyline.Count > 6:
recursiveHex(hexPolyline, length, recursion)
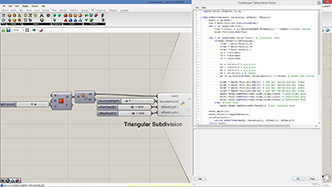
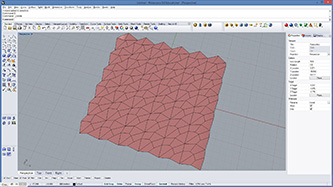
# this subdivided mesh faces by recursive function
# input type - Mesh (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
import math
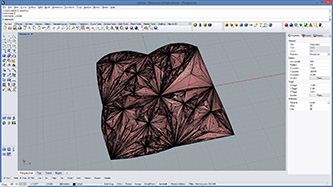
def subdivide(pt1, pt2, pt3, depth, resultList):
if(depth == 0 or random.random()<0.1): # random omission
v1 = rg.Point3f(pt1.X, pt1.Y, pt1.Z);
v2 = rg.Point3f(pt2.X, pt2.Y, pt2.Z);
v3 = rg.Point3f(pt3.X, pt3.Y, pt3.Z);
resultList.append([v1,v2,v3])
else:
npt1 = (pt1+pt2)/2
npt2 = (pt2+pt3)/2
npt3 = (pt3+pt1)/2
npt4 = (npt1+npt2+npt3)/3
normal = normalVector(pt1,pt2,pt3)
npt4 += normal*0.06*math.sqrt(depth)
subdivide(npt1, pt1, npt3, depth-1, resultList)
subdivide(npt2, pt2, npt1, depth-1, resultList)
subdivide(npt3, pt3, npt2, depth-1, resultList)
subdivide(npt1, npt2, npt4, depth-1, resultList)
subdivide(npt2, npt3, npt4, depth-1, resultList)
subdivide(npt3, npt1, npt4, depth-1, resultList)
def normalVector(pt1, pt2, pt3):
vec1 = rg.Vector3d.Subtract(rg.Vector3d(pt2),rg.Vector3d(pt1))
vec2 = rg.Vector3d.Subtract(rg.Vector3d(pt3),rg.Vector3d(pt1))
return rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(vec1, vec2)
# main
a = []
vertices = []
for face in mesh.Faces:
pt1 = rg.Vector3d(mesh.Vertices[face.A])
pt2 = rg.Vector3d(mesh.Vertices[face.B])
pt3 = rg.Vector3d(mesh.Vertices[face.C])
subdivide(pt1, pt2, pt3, 5, vertices)
if(face.IsQuad):
pt4 = rg.Vector3d(mesh.Vertices[face.D])
subdivide(pt1, pt4, pt3, 5, vertices) # reverse order
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
for vtx in vertices:
idx = mesh2.Vertices.Count
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx[0])
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx[1])
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx[2])
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(idx, idx+1, idx+2)
a = mesh2
# bake points with colors
# input type - bool (Item Access)
import scriptcontext as sc
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
if bake:
xnum = 100
ynum = 100
for i in range(xnum):
for j in range(ynum):
pt = rg.Point3d(i,j,0)
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr.ColorSource = rd.ObjectColorSource.ColorFromObject
attr.ObjectColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(i/xnum*255, j/ynum*255, 0)
sc.doc.Objects.AddPoint(pt, attr)
# bake curves with colors
# input type - bool (Item Access)
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
import math
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
if bake:
num = 100
for i in range(num):
pt1 = rg.Point3d(i, 0, math.sin(i*0.2)*2)
pt2 = rg.Point3d(i, 5, 2)
pt3 = rg.Point3d(i, 10, math.cos(i*0.1)*2)
curve = rg.NurbsCurve.Create(False, 2, [pt1, pt2, pt3])
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr.ColorSource = rd.ObjectColorSource.ColorFromObject
attr.ObjectColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(i/num*255, (num-i)/num*255, 255)
sc.doc.Objects.AddCurve(curve, attr)
# bake surfaces with simple materials
# input type - bool (Item Access)
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
if bake:
xnum = 20
ynum = 20
for i in range(xnum):
for j in range(ynum):
pt1 = rg.Point3d(i, j, 0)
pt2 = rg.Point3d(i+1, j, 0)
pt3 = rg.Point3d(i+1, j+1, i*j/100)
pt4 = rg.Point3d(i, j+1, 0)
surface = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt1,pt2,pt3,pt4)
materialIndex = sc.doc.Materials.Add()
material = sc.doc.Materials[materialIndex]
material.DiffuseColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(i/xnum*255, j/ynum*255, 255)
material.CommitChanges()
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr.MaterialSource = rd.ObjectMaterialSource.MaterialFromObject
attr.MaterialIndex = materialIndex
sc.doc.Objects.AddSurface(surface, attr)
# bake breps with simple materials
# input type - bool (Item Access)
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
if bake:
xnum = 10
ynum = 10
znum = 10
for i in range(xnum):
for j in range(ynum):
for k in range(znum):
size = (i/xnum+j/ynum+k/znum)/3
box = rg.Box( rg.Plane.WorldXY, rg.Interval(i, i+size), rg.Interval(j,j+size), rg.Interval(k, k+size) )
brep = rg.Brep.CreateFromBox(box)
materialIndex = sc.doc.Materials.Add()
material = sc.doc.Materials[materialIndex]
material.DiffuseColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(i/xnum*255, j/ynum*255, k/znum*255)
material.CommitChanges()
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr.MaterialSource = rd.ObjectMaterialSource.MaterialFromObject
attr.MaterialIndex = materialIndex
sc.doc.Objects.AddBrep(brep, attr)
# material attributes
# input type - bool (Item Access)
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
if bake:
xnum = 20
ynum = 20
for i in range(xnum):
for j in range(ynum):
pt = rg.Point3d(i, j, 0)
sphere = rg.Sphere(pt, 0.4)
surface = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromSphere(sphere)
materialIndex = sc.doc.Materials.Add()
material = sc.doc.Materials[materialIndex]
material.AmbientColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 0)
material.DiffuseColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(255, 0, 0)
material.EmissionColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(0, j/ynum*255, 0)
material.ReflectionColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(255, 255, 255)
material.SpecularColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(255, 255, i/xnum*255)
material.Transparency = i/xnum
material.TransparentColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 255)
material.Shine = 1
material.CommitChanges()
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr.MaterialSource = rd.ObjectMaterialSource.MaterialFromObject
attr.MaterialIndex = materialIndex
sc.doc.Objects.AddSurface(surface, attr)
# setting materials by name
# input type - materialName: str, bake: bool (Item Access)
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
if bake:
xnum = 20
ynum = 20
for i in range(xnum):
for j in range(ynum):
pt = rg.Point3d(i, j, 0)
sphere = rg.Sphere(pt, 0.4)
surface = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromSphere(sphere)
materialIndex = sc.doc.Materials.Find(materialName, True)
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
if materialIndex >= 0:
attr.MaterialSource = rd.ObjectMaterialSource.MaterialFromObject
attr.MaterialIndex = materialIndex
else:
print "material " + materialName + " not found"
sc.doc.Objects.AddSurface(surface, attr)
# baking into layers
# input type - bool (Item Access)
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
import math
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
if bake:
num = 40
for i in range(num):
pt1 = rg.Point3d(-math.sin(i*0.2), -math.sin(i*0.2), i*0.2)
pt2 = rg.Point3d(math.cos(i*0.2), -math.sin(i*0.2), i*0.2)
pt3 = rg.Point3d(math.sin(i*0.2), math.cos(i*0.2), i*0.2)
pt4 = rg.Point3d(-math.cos(i*0.2), math.sin(i*0.2), i*0.2)
curve = rg.NurbsCurve.Create(True, 1, [pt1, pt2, pt3, pt4])
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr.ColorSource = rd.ObjectColorSource.ColorFromObject
attr.ObjectColor = sd.Color.FromArgb((num-i)/num*255, 255, i/num*255)
layerName = "layer_" + str(i)
layerIndex = sc.doc.Layers.Find(layerName, True)
if layerIndex < 0:
layer = rd.Layer()
layer.Name = layerName
layerIndex = sc.doc.Layers.Add(layer)
attr.LayerIndex = layerIndex
sc.doc.Objects.AddCurve(curve, attr)
# bake objects with attributes
# input type - obj: GeometryBase, objName: str, layerName: str, displayColor: Color, plotColor: Color, plotWeight: float, ambientColor: color, diffuseColor: Color, emissionColor: Color, specularColor: Color, transparency: float, shine: float, wireDensity: int, bake: bool (Item Access)
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
if bake and obj is not None:
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
if objName is not None: # setting object name
attr.Name = objName
if layerName is not None: # setting layer
if rd.Layer.IsValidName(layerName):
layerIndex = sc.doc.Layers.Find(layerName, True)
if layerIndex < 0: # if the layer doesn't exist
layer = rd.Layer()
layer.Name = layerName
layerIndex = sc.doc.Layers.Add(layer)
attr.LayerIndex = layerIndex
if displayColor is not None: # setting display color
attr.ColorSource = rd.ObjectAttributes.ColorSource.PropertyType.ColorFromObject
attr.ObjectColor = displayColor
if plotColor is not None: # setting plot color
attr.PlotColorSource = rd.ObjectAttributes.PlotColorSource.PropertyType.PlotColorFromObject
attr.PlotColor = plotColor
if plotWeight >= 0: # setting plot weight
attr.PlotWeightSource = rd.ObjectAttributes.PlotWeightSource.PropertyType.PlotWeightFromObject
attr.PlotWeight = plotWeight
if ambientColor is not None or diffuseColor is not None or emissionColor is not None or specularColor is not None or transparency >= 0 or shine >=0: # setting material
materialIndex = sc.doc.Materials.Add()
material = sc.doc.Materials[materialIndex]
if ambientColor is not None:
material.AmbientColor = ambientColor
if diffuseColor is not None:
material.DiffuseColor = diffuseColor
if emissionColor is not None:
material.EmissionColor = emissionColor
if specularColor is not None:
material.SpecularColor = specularColor
if transparency >= 0:
material.Transparency = transparency
if shine >= 0:
material.Shine = shine
material.CommitChanges()
attr.MaterialSource = rd.ObjectMaterialSource.MaterialFromObject
attr.MaterialIndex = materialIndex
if wireDensity > 0 or wireDensity == -1: # setting wire density
attr.WireDensity = wireDensity
# bake by type
type = obj.ObjectType
if type == rd.ObjectType.Point:
sc.doc.Objects.AddPoint(obj.Location, attr)
elif type == rd.ObjectType.Curve:
sc.doc.Objects.AddCurve(obj, attr)
elif type == rd.ObjectType.Surface:
sc.doc.Objects.AddSurface(obj, attr)
elif type == rd.ObjectType.Brep:
sc.doc.Objects.AddBrep(obj, attr)
elif type == rd.ObjectType.Mesh:
sc.doc.Objects.AddMesh(obj, attr)
else:
print "object type "+str(type)+ " is not baked"
# Panelization with materials
# input type: surf : Surface, unum : int, vnum : int, bake : bool
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
import math
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
panels = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
u = i/unum
v = j/vnum
pt1 = surf.PointAt(u, v)
pt2 = surf.PointAt(u + (2-u)/unum, v + 0.1/vnum)
pt3 = surf.PointAt(u + (1.5+u)/unum, v + 1/vnum)
pt4 = surf.PointAt(u + 0.3/unum, v + 1/vnum)
n1 = surf.NormalAt(u, v)
n2 = surf.NormalAt(u + (2.5-u)/unum, v + 0.1/vnum)
n3 = surf.NormalAt(u + (1.5+u)/unum, v + 1/vnum)
n4 = surf.NormalAt(u + 0.3/unum, v + 1/vnum)
pt1 += n1*0.2
pt2 += n2*1.2
pt3 += n3*1.8
pt4 += n4*0.3
panel = rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromCorners(pt1, pt2, pt3, pt4)
panels.append(panel)
if bake:
materialIndex = sc.doc.Materials.Add()
material = sc.doc.Materials[materialIndex]
material.AmbientColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(0, 0, 0)
material.DiffuseColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(255-u*255, u*255, math.fabs(1-2*v)*255)
material.EmissionColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(0, u*30, 0)
material.SpecularColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(u*255, 0, u*255)
material.Transparency = u
material.Shine = 1-u
material.CommitChanges()
attr = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr.MaterialSource = rd.ObjectMaterialSource.MaterialFromObject
attr.MaterialIndex = materialIndex
sc.doc.Objects.AddSurface(panel, attr)
# This makes surface panels by 3 points on an input surface
# input type: surf - Surface, unum - int, vnum - int
# This makes surface panels by 3 points on an input surface
# input type: surf - Surface, unum - int, vnum - int
import scriptcontext as sc
import System.Drawing as sd
import Rhino.DocObjects as rd
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import Rhino
import math
def stretchTriangle(pt1, pt2, pt3, nml, stretchRatio):
pt4 = pt2 + (pt2-pt1)*stretchRatio + nml
return rg.NurbsSurface.CreateFromPoints([pt1,pt2,pt4, pt3,pt2,pt4], 2, 3, 1, 2)
sc.doc = Rhino.RhinoDoc.ActiveDoc
panels = []
for i in range(unum):
for j in range(vnum):
if (i+j)%2 == 0:
u = i/unum
v = j/vnum
pt1 = surf.PointAt(u, v)
pt2 = surf.PointAt(u + 1/unum, v - 1/vnum)
pt3 = surf.PointAt(u + 1/unum, v + 1/vnum)
pt4 = surf.PointAt(u + 1/unum, v + 0.5/vnum)
nml = surf.NormalAt(u, v)
panel1 = stretchTriangle(pt1, pt2, pt3+nml*0.5, nml*2*u, 4*u+0.5)
panels.append(panel1)
panel2 = stretchTriangle(pt1, pt4, pt2, nml*u, 2*u+0.5)
panels.append(panel2)
if bake:
materialIndex1 = sc.doc.Materials.Add()
material1 = sc.doc.Materials[materialIndex1]
if (i+j)%4 == 0:
material1.DiffuseColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(255-u*255, u*255, math.fabs(1-2*v)*255)
material1.EmissionColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(0, u*30, 0)
material1.SpecularColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(u*255, 0, u*255)
material1.Shine = 0.25
else:
material1.DiffuseColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(0,0,128)
material1.Transparency = 0.25
material1.CommitChanges()
attr1 = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr1.MaterialSource = rd.ObjectMaterialSource.MaterialFromObject
attr1.MaterialIndex = materialIndex1
sc.doc.Objects.AddSurface(panel1, attr1)
materialIndex2 = sc.doc.Materials.Add()
material2 = sc.doc.Materials[materialIndex2]
material2.DiffuseColor = sd.Color.FromArgb(math.fabs(1-2*v)*255, (1-math.fabs(1-2*v))*128, 0)
material2.CommitChanges()
attr2 = rd.ObjectAttributes()
attr2.MaterialSource = rd.ObjectMaterialSource.MaterialFromObject
attr2.MaterialIndex = materialIndex2
sc.doc.Objects.AddSurface(panel2, attr2)
# defining a custom class
# input type - Point3d (List Access)
class Class1:
# __init__ is a special method to initialize a class instance (constructor)
def __init__(self, pt):
self.center = pt
for pt in pts:
obj = Class1(pt)
# defining a custom class
# input type - Point3d (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
class Class1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.center = pt
self.radius = 0.5
def getCircle(self):
circle = rs.AddCircle(self.center, self.radius)
a.append(circle)
a = []
for pt in pts:
obj = Class1(pt)
obj.getCircle()
# defining a custom class
# input type - Point3d (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
class Class1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.center = pt
self.radius = 0.5
def getCircle(self):
return rs.AddCircle(self.center, self.radius) # returns a circle
a = []
for pt in pts:
obj = Class1(pt)
a.append( obj.getCircle() )
# defining a custom class
# input type - Point3d (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
class Class1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.center = pt
self.radius = 0.5
def getCircle(self):
return rs.AddCircle(self.center, self.radius)
def getSquare(self):
plane = rg.Plane(self.center + rg.Point3d(-self.radius,-self.radius,0),rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
return rs.AddRectangle(plane, self.radius*2, self.radius*2)
a = []
for pt in pts:
obj = Class1(pt)
a.append( obj.getCircle() )
a.append( obj.getSquare() )
# defining a custom class
# input type - Point3d (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
class CircleSequence:
def __init__(self, pt, dir):
self.center = pt
self.dir = dir
self.radius = 0.2
def generate(self):
for i in range(10):
circle = rs.AddCircle(self.center, self.radius)
self.dir *= 0.9
self.radius *= 0.8
self.dir.Rotate(0.2, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
self.center += self.dir
a.append(circle)
a = []
for pt in pts:
obj = CircleSequence(pt, rg.Vector3d(0,0.2,0))
obj.generate()
# defining a custom class
# input type - Point3d (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
import math
class CircleSequence:
def __init__(self, pt, dir):
self.center = pt
self.dir = dir
self.radius = 0.2
def generate(self):
for i in range(10):
circle = rs.AddCircle(self.center, self.radius)
self.dir *= 0.9
self.radius *= 0.8
self.dir.Rotate(0.2, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
self.center += self.dir
a.append(circle)
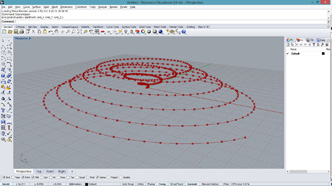
class SpiralCircles:
def __init__(self, pt, size, count):
self.center = pt
dir = rg.Vector3d(0,size,0)
self.arms = []
for i in range(count):
arm = CircleSequence(pt, rg.Vector3d(dir))
self.arms.append(arm)
dir.Rotate(math.pi*2/count, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
def generate(self):
for arm in self.arms:
arm.generate()
a = []
for pt in pts:
size = random.random()*0.3 + 0.1
count = int(random.random()*10)+2
obj = SpiralCircles(pt, size, count)
obj.generate()
# defining a custom class
# input type - Point3d (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
class HierarchyBoxes:
def __init__(self, pt, size, level):
self.pt = pt
self.size = size
self.child = CornerBoxes(pt, size, size/2, level-1)
def generate(self):
box = rg.Box(rg.Plane.WorldXY, [self.pt, rg.Point3d(pt)+rg.Point3d(self.size,self.size,self.size)])
a.append(box)
self.child.generate()
class CornerBoxes:
def __init__(self, pt, size1, size2, level):
self.pt = pt
self.size1 = size1
self.size2 = size2
self.children = []
if(level>1):
child1 = CornerBoxes(rg.Point3d(pt)+rg.Point3d(-size2,-size2,-size2), size2, size2/2, level-1)
child2 = CornerBoxes(rg.Point3d(pt)+rg.Point3d(size1,-size2,-size2), size2, size2/2, level-1)
child3 = CornerBoxes(rg.Point3d(pt)+rg.Point3d(-size2,size1,-size2), size2, size2/2, level-1)
self.children.append(child1)
self.children.append(child2)
self.children.append(child3)
def makeBox(self, corner):
box = rg.Box(rg.Plane.WorldXY, [corner, rg.Point3d(corner)+rg.Point3d(-self.size2,-self.size2,-self.size2)])
a.append(box)
def generate(self):
self.makeBox(self.pt)
self.makeBox(rg.Point3d(self.pt) + rg.Point3d(self.size1+self.size2, 0, 0))
self.makeBox(rg.Point3d(self.pt) + rg.Point3d(0, self.size1+self.size2, 0))
for c in self.children:
c.generate()
a = []
for pt in pts:
level = int(random.random()*5)+1
obj = HierarchyBoxes(pt, 0.5, level)
obj.generate()
# defining a custom class
# input type - Point3d (List Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
class AngleSequence:
def __init__(self, pt, dir, width, count):
self.pt = pt
self.width = width
self.dir = dir
self.count = count
def generate(self):
ndir = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(self.dir, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
wdir = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(self.dir, ndir)
wdir.Unitize()
wdir *= self.width/2
pt1 = rg.Point3d(self.pt)-wdir
pt2 = rg.Point3d(self.pt)
pt3 = rg.Point3d(self.pt)+wdir
plines = []
for i in range(self.count):
pline = rg.PolylineCurve([pt1,pt2,pt3])
plines.append(pline)
a.append(pline)
pt1 += self.dir
pt2 += self.dir*1.5
pt3 += self.dir
return plines
class TiltedExtrusion:
def __init__(self, pt, dir, width, count):
self.angles = AngleSequence(pt,dir,width,count)
self.dir = rg.Vector3d(dir)
def loft(self, pline, dir):
pline2 = pline.Duplicate()
pline2.Translate(dir.X, dir.Y, dir.Z)
brep = rg.Brep.CreateFromLoft([pline,pline2], rg.Point3d.Unset, rg.Point3d.Unset, rg.LoftType.Straight, False)
a.extend(brep)
def generate(self):
plines = self.angles.generate()
for pl in plines:
self.loft(pl, self.dir)
self.dir.Rotate(0.1, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
self.dir *= 0.95
class SpiralAggregation:
def __init__(self, pt, count):
self.children = []
dir = rg.Vector3d(0.2, 0, 0.01)
for i in range(count):
len = int(random.random()*5)+10
width = random.random()*1.5+1.0
extrusion = TiltedExtrusion(rg.Point3d(pt), rg.Vector3d(dir)+rg.Vector3d(0,0,0.08), width, len)
self.children.append(extrusion)
dir.Rotate(0.5, rg.Vector3d.ZAxis)
pt += dir*len
def generate(self):
for c in self.children:
c.generate()
a = []
for pt in pts:
obj = SpiralAggregation(pt, 100)
obj.generate()
# defining a connective module
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
class Module1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.pt = pt
self.links = []
def connect(self, modules):
for m in modules:
if m is not self:
dist = m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt)
if dist < threshold:
self.links.append(m)
def generate(self):
for m in self.links:
line = rs.AddLine(self.pt, m.pt)
lines.append(line)
lines = []
modules = []
# create modules
for pt in pts:
m = Module1(pt)
modules.append(m)
# connect modules
for m in modules:
m.connect(modules)
# generate geometries
for m in modules:
m.generate()
# defining a connective module
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float (Item Access), maxLink : int (Item Access)
# defining a connective module
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
class Module1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.pt = pt
self.links = []
def connect(self, modules):
#sort list by distance
sorted(modules, key=lambda m: m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt))
for m in modules:
if len(self.links) >= maxLink:
break
if m is not self and m not in self.links:
dist = m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt)
if dist < threshold and len(m.links) < maxLink:
self.links.append(m)
m.links.append(self)
def generate(self):
for m in self.links:
line = rs.AddLine(self.pt, m.pt)
lines.append(line)
lines = []
modules = []
for pt in pts:
m = Module1(pt)
modules.append(m)
for m in modules:
m.connect(modules)
for m in modules:
m.generate()
# defining a connective module
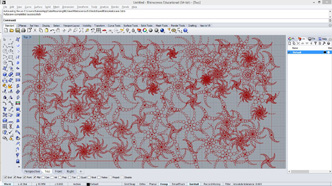
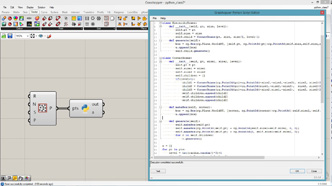
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float (Item Access), maxLink : int (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
# importing grasshopper tree classes
import clr
clr.AddReference("Grasshopper")
from Grasshopper.Kernel.Data import GH_Path
from Grasshopper import DataTree
class Module1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.pt = pt
self.links = []
def connect(self, modules):
sorted(modules, key=lambda m: m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt))
for m in modules:
if len(self.links) >= maxLink:
break # finish loop
if m is not self and m not in self.links:
dist = m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt)
if dist < threshold and len(m.links) < maxLink:
self.links.append(m)
m.links.append(self)
def generate(self):
id = center.BranchCount
center.Add(self.pt, GH_Path(id)) # add one data in a branch
linkNum = len(self.links)
armPts = []
for i in range(linkNum):
pt2 = (self.pt + self.links[i].pt)/2 # mid point
armPts.append(pt2)
arm.AddRange(armPts, GH_Path(id)) # add multiple data in a branch
# initialize output points in tree structure
center = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
arm = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
modules = []
for pt in pts:
m = Module1(pt)
modules.append(m)
for m in modules:
m.connect(modules)
for m in modules:
m.generate()
# defining a connective module
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float (Item Access), maxLink : int (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import clr
clr.AddReference("Grasshopper")
from Grasshopper.Kernel.Data import GH_Path
from Grasshopper import DataTree
class Module1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.pt = pt
self.links = []
def connect(self, modules):
sorted(modules, key=lambda m: m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt))
for m in modules:
if len(self.links) >= maxLink:
break
if m is not self and m not in self.links:
dist = m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt)
if dist < threshold and len(m.links) < maxLink:
self.links.append(m)
m.links.append(self)
def generate(self):
id = center.BranchCount
center.Add(self.pt, GH_Path(id))
linkNum = len(self.links)
for i in range(linkNum):
pt2 = (self.pt + self.links[i].pt)/2 # mid point
for j in range(i+1, linkNum):
pt3 = (self.pt + self.links[j].pt)/2 # mid point
arm3Pts.AddRange([pt2, self.pt, pt3], GH_Path(id,i,j)) # add 2 arm and center
center = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
arm3Pts = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
modules = []
for pt in pts:
m = Module1(pt)
modules.append(m)
for m in modules:
m.connect(modules)
for m in modules:
m.generate()
# defining a connective module
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float (Item Access), maxLink : int (Item Access)# importing grasshopper tree classes
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import clr
clr.AddReference("Grasshopper")
from Grasshopper.Kernel.Data import GH_Path
from Grasshopper import DataTree
class Module1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.pt = pt
self.links = []
def connect(self, modules):
#sort list by distance
sorted(modules, key=lambda m: m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt))
for m in modules:
if len(self.links) >= maxLink:
break # finish loop
if m is not self and m not in self.links:
dist = m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt)
if dist < threshold and len(m.links) < maxLink:
self.links.append(m)
m.links.append(self)
def generate(self):
id = center.BranchCount
center.Add(self.pt, GH_Path(id))
linkNum = len(self.links)
for i in range(linkNum):
pt2 = (self.pt + self.links[i].pt)/2
for j in range(i+1, linkNum):
pt3 = (self.pt + self.links[j].pt)/2
for k in range(j+1, linkNum):
pt4 = (self.pt + self.links[k].pt)/2
armFacePts.AddRange([pt2, pt3, pt4], GH_Path(id,i,j,k)) # add 3 face pts
center = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
armFacePts = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
modules = []
for pt in pts:
m = Module1(pt)
modules.append(m)
for m in modules:
m.connect(modules)
for m in modules:
m.generate()
# defining a connective module
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float (Item Access), maxLink : int (Item Access), depthRatio : float (Item Access), shrinkRatio : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import clr
clr.AddReference("Grasshopper")
from Grasshopper.Kernel.Data import GH_Path
from Grasshopper import DataTree
class Module1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.pt = pt
self.links = []
def connect(self, modules):
#sort list by distance
sorted(modules, key=lambda m: m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt))
for m in modules:
if len(self.links) >= maxLink:
break
if m is not self and m not in self.links:
dist = m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt)
if dist < threshold and len(m.links) < maxLink:
self.links.append(m)
m.links.append(self)
def generate(self):
linkNum = len(self.links)
if linkNum != 3:
return # do nothing if less than 3 links
self.armLength = 0 # total distance to links
for m in self.links:
self.armLength += m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt)
tricenter = (self.links[0].pt+self.links[1].pt+self.links[2].pt)/3 # center of triangle
normal = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(self.links[1].pt-self.links[0].pt, self.links[2].pt-self.links[0].pt) # normal vector of triangle
normal.Unitize()
normal *= self.armLength * depthRatio # normal depth is changed by link distance
for i in range(linkNum):
spts = []
spts.append( (self.links[i].pt + self.pt)/2 ) # mid point
sp = self.links[i].pt * 0.4 + self.pt * 0.6 # first radial point
spts.append(sp)
for j in range(30): # generating spiral points
vec = sp - self.pt
vec.Rotate(0.5, normal)
sp = vec*shrinkRatio + self.pt + normal/30
spts.append(sp)
spiralPts.AddRange(spts, GH_Path(self.id, i)) # using id number
spiralPts = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
modules = []
for pt in pts:
m = Module1(pt)
m.id = len(modules) # setting id number
modules.append(m)
for m in modules:
m.connect(modules)
for m in modules:
m.generate()
# defining a connective module
# input type - pts : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float (Item Access), maxLink : int (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
import clr
clr.AddReference("Grasshopper")
from Grasshopper.Kernel.Data import GH_Path
from Grasshopper import DataTree
class Module1:
def __init__(self, pt):
self.pt = pt
self.links = []
if random.random()<0.5:
self.type = 1
else:
self.type = 2
def connect(self, modules):
#sort list by distance
sorted(modules, key=lambda m: m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt))
for m in modules:
if len(self.links) >= maxLink:
break
if m is not self and m not in self.links:
dist = m.pt.DistanceTo(self.pt)
if dist < threshold and len(m.links) < maxLink:
self.links.append(m)
m.links.append(self)
def generate(self):
linkNum = len(self.links)
if self.type == 1:
center1.Add(self.pt, GH_Path(self.id))
else:
center2.Add(self.pt, GH_Path(self.id))
for i in range(linkNum):
mpt = (self.pt + self.links[i].pt)/2
if self.type == 1 and self.links[i].type == 1: # link 1-1
arm1_1.AddRange([mpt, self.pt], GH_Path(self.id, i))
elif self.type == 1 and self.links[i].type == 2: #link 1-2
arm1_2.AddRange([mpt, self.pt], GH_Path(self.id, i))
elif self.type == 2 and self.links[i].type == 1: #link 2-1
arm2_1.AddRange([mpt, self.pt], GH_Path(self.id, i))
elif self.type == 2 and self.links[i].type == 2: #link 2-2
arm2_2.AddRange([mpt, self.pt], GH_Path(self.id, i))
center1 = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
center2 = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
arm1_1 = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
arm1_2 = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
arm2_1 = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
arm2_2 = DataTree[rg.Point3d]()
modules = []
for pt in pts:
m = Module1(pt)
m.id = len(modules) # setting id number
modules.append(m)
for m in modules:
m.connect(modules)
for m in modules:
m.generate()
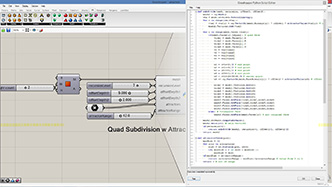
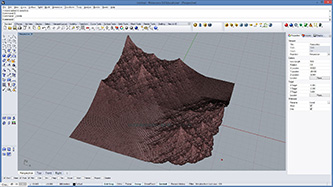
# offset each vertex randomly and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), depth : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def offsetVertex(mesh):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray() # get all vertices in a list
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * depth * random.random() #offset randomly
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFaces(mesh.Faces) # add all faces at once
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
return mesh2
a = offsetVertex(mesh)
# move each vertex randomly and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), depth : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def randomizeVertex(mesh):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray() # get all vertices in a list
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(random.uniform(-1,1)*depth, random.uniform(-1,1)*depth, random.uniform(-1,1)*depth) #random xyz move
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFaces(mesh.Faces) # add all faces at once
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
return mesh2
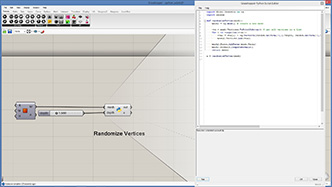
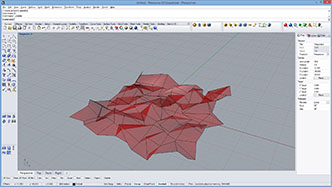
a = randomizeVertex(mesh)
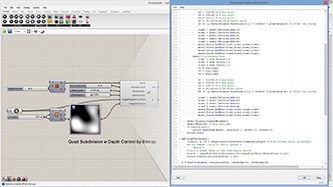
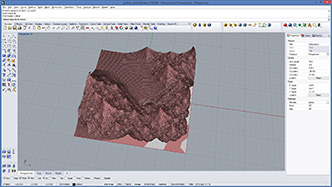
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), depth : float (Item Access), atractors : Point3d (List Access), threshold : float (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def moveVertexByAttractor(mesh):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + attractorVector(vtx[i]) * depth #add attractor vector
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFaces(mesh.Faces)
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
return mesh2
def attractorVector(pos):
minDist = -1
for attr in attractors: # find closest attractor
dist = rs.Distance(pos, attr)
if( minDist < 0 or dist < minDist ):
minDist = dist
closest = attr
if(minDist < threshold):
vec = pos - closest
vec *= (threshold - minDist)/(threshold) # length from 0 to 1
vec.Unitize()
return vec
return rg.Vector3d(0,0,0) # return zero vector if out of threshold
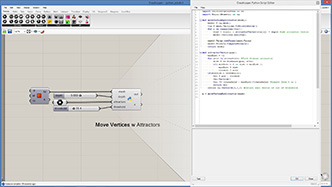
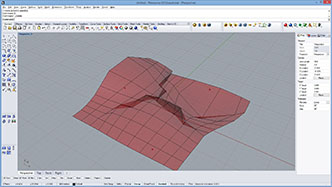
a = moveVertexByAttractor(mesh)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
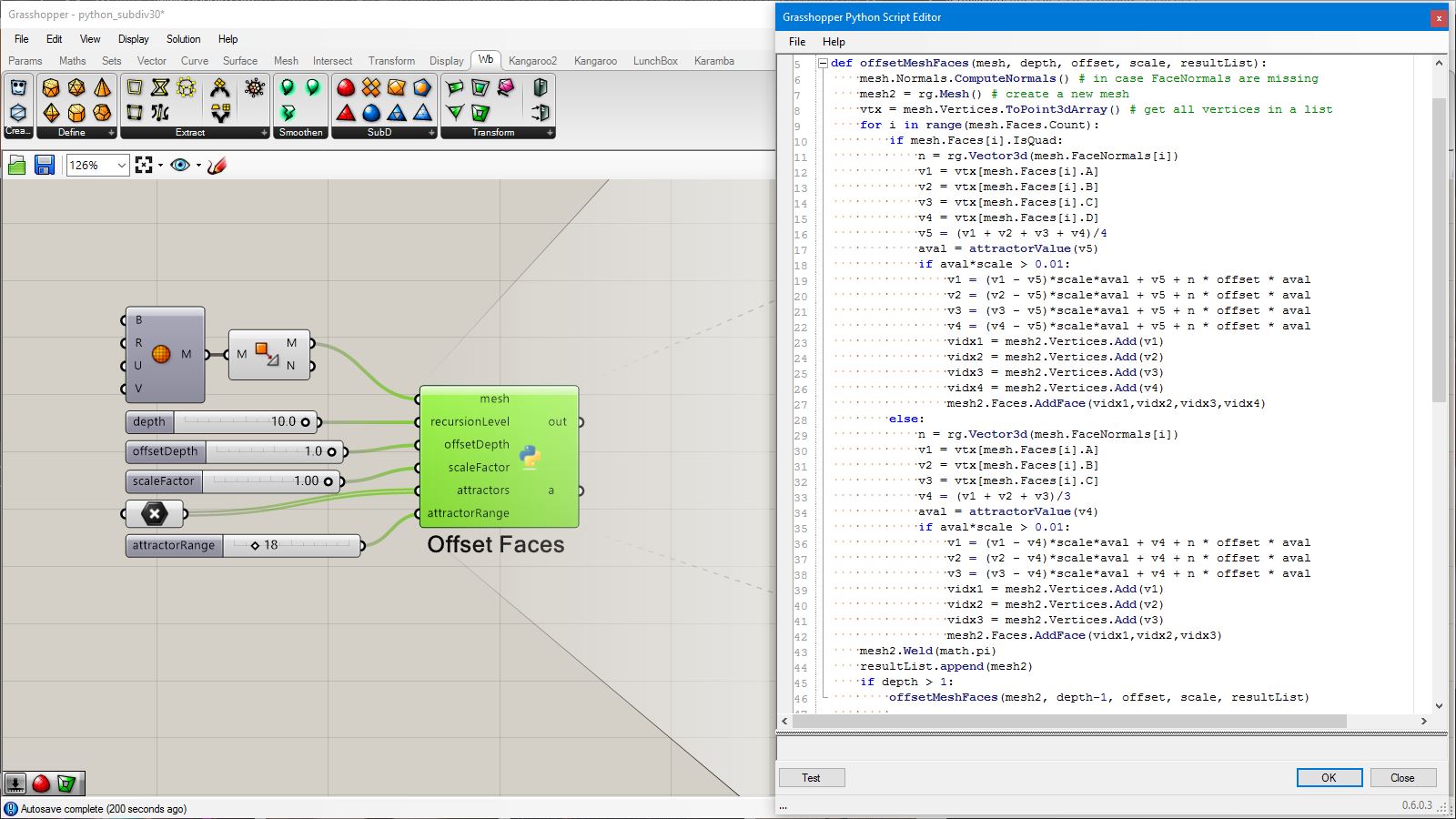
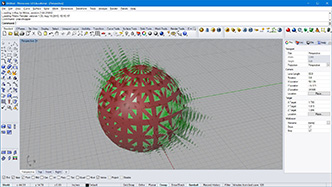
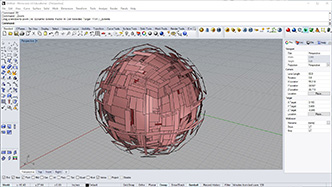
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recureionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
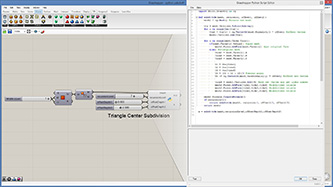
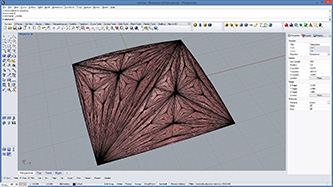
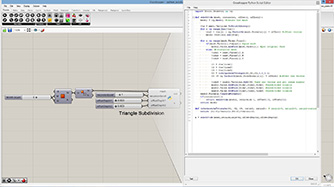
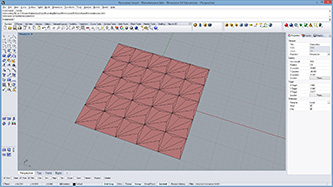
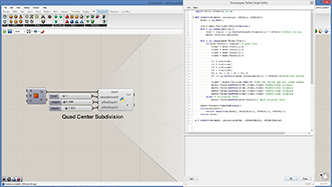
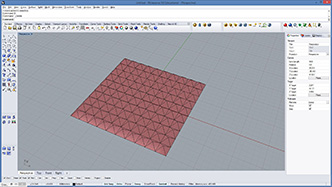
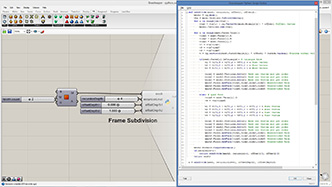
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() #create new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 #offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): #quad mesh
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) #put original face
else: #triangular mesh
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = (v1 + v2 + v3)/3 #center point
v4 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 #offset new vertex
vidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4) #add new vertex and get index number
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh,recursionLevel,offsetDepth1,offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() #create new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 #offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): #quad mesh
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) #put original face
else: #triangular mesh
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3,0.4,0.5) # point inside triangle
v4 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 #offset new vertex
vidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4) #add new vertex and get index number
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
def interpolateTriangle(v1, v2, v3, ratio1, ratio2): # ratio1 > 0, ratio2 > 0, ratio1+ratio2 < 1 to be inside triangle
return (v2-v1)*ratio1+(v3-v1)*ratio2+v1
a = subdivide(mesh,recursionLevel,offsetDepth1,offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
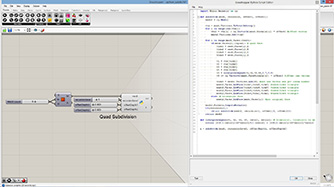
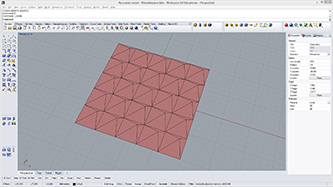
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 #offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
v5 = (v1 + v2 + v3 + v4)/4
v5 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 #offset new vertex
vidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v5) #add new vertex and get index number
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx5) #subdivided triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx5) #subdivided triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,vidx5) #subdivided triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,vidx5) #subdivided triangle
else: # triangular face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) #put original face
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), recursionProbability : float (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 #offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
v5 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,0.7,0.9) # point inside quad
v5 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 #offset new vertex
vidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v5) #add new vertex and get index number
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx5) #subdivided triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx5) #subdivided triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,vidx5) #subdivided triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,vidx5) #subdivided triangle
else: # triangular face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) # put original face
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
def interpolateQuad(v1, v2, v3, v4, ratio1, ratio2): # 0 < ratio1 < 1, 0 < ratio2 < 1 to be inside quad
return (v1*(1-ratio1)+v2*ratio1)*(1-ratio2) + (v4*(1-ratio1)+v3*ratio1)*ratio2
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad : # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2
w1 = interpolateLine(v1,v2,0.2) # interpolation on edge
w2 = interpolateLine(v1,v2,0.4) + n # interpolate on edge and offset
w3 = interpolateLine(v1,v2,0.6) + n # interpolate on edge and offset
w4 = interpolateLine(v1,v2,0.8) # interpolation on edge
w5 = interpolateLine(v4,v3,0.2) # interpolation on edge
w6 = interpolateLine(v4,v3,0.4) + n # interpolate on edge and offset
w7 = interpolateLine(v4,v3,0.6) + n # interpolate on edge and offset
w8 = interpolateLine(v4,v3,0.8) # interpolation on edge
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3)
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4)
widx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w5)
widx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w6)
widx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w7)
widx8 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w8)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx5,vidx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,widx2,widx6,widx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx2,widx3,widx7,widx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx3,widx4,widx8,widx7)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx4,vidx2,vidx3,widx8)
else: # triangular face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(180)
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
def interpolateLine(v1, v2, ratio): # 0 < ratio < 1
return v1*(1-ratio) + v2*ratio
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
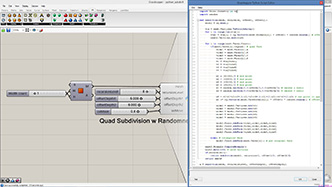
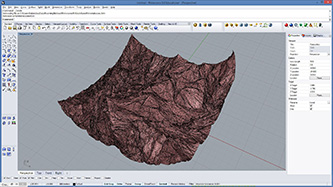
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), recursionProbability : float (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() #create new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 #offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): #quad mesh
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) #put original face
else: #triangular mesh
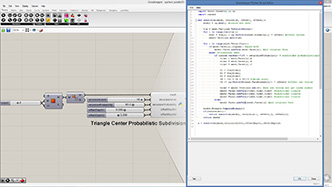
if random.random()*100 < recursionProbability: # subdivided probabilistically
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
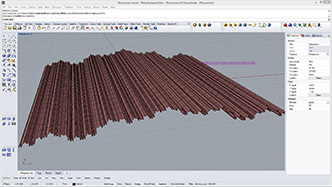
v4 = (v1 + v2 + v3)/3 #center point
v4 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 #offset new vertex
vidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4) #add new vertex and get index number
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,vidx4) #subdivided trianle
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) #put original face
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh,recursionLevel,offsetDepth1,offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 #offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 * random.random() #random normal vector
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsTriangle): # triangle face
w1 = v1*0.6 + v2*0.2 + v3*0.2 + n #new vertex
w2 = v1*0.2 + v2*0.6 + v3*0.2 + n #new vertex
w3 = v1*0.2 + v2*0.2 + v3*0.6 + n #new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1) #add new vertex and get index
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2) #add new vertex and get index
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3) #add new vertex and get index
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1) #subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx3,widx2) #subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,widx1,widx3) #subdivided face
else: # quad face
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
w1 = v1*0.4 + v2*0.2 + v3*0.2 + v4*0.2 + n #new vertex
w2 = v1*0.2 + v2*0.4 + v3*0.2 + v4*0.2 + n #new vertex
w3 = v1*0.2 + v2*0.2 + v3*0.4 + v4*0.2 + n #new vertex
w4 = v1*0.2 + v2*0.2 + v3*0.2 + v4*0.4 + n #new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1) #add new vertex and get index
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2) #add new vertex and get index
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3) #add new vertex and get index
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4) #add new vertex and get index
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1) #subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx3,widx2) #subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,widx4,widx3) #subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,widx1,widx4) #subdivided face
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), recursionProbability : float (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access), holeRatio : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 # offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 * random.random() # random normal vector
if random.random()*100 < recursionProbability :
if mesh.Faces[i].IsTriangle: # triangle face
w1 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, holeRatio/3,holeRatio/3) + n # new vertex
w2 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, 1-holeRatio*2/3,holeRatio/3) + n # new vertex
w3 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, holeRatio/3,1-holeRatio*2/3) + n # new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1) # add new vertex and get index
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2) # add new vertex and get index
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3) # add new vertex and get index
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx3,widx2) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,widx1,widx3) # subdivided face
else: # quad face
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
w1 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,holeRatio/2,holeRatio/2) + n # new vertex
w2 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,1-holeRatio/2,holeRatio/2) + n # new vertex
w3 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,1-holeRatio/2,1-holeRatio/2) + n # new vertex
w4 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,holeRatio/2,1-holeRatio/2) + n # new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1) # add new vertex and get index
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2) # add new vertex and get index
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3) # add new vertex and get index
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4) # add new vertex and get index
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx3,widx2) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,widx4,widx3) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,widx1,widx4) # subdivided face
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
def interpolateQuad(v1, v2, v3, v4, ratio1, ratio2): # 0 < ratio1 < 1, 0 < ratio2 < 1 to be inside quad
return (v1*(1-ratio1)+v2*ratio1)*(1-ratio2) + (v4*(1-ratio1)+v3*ratio1)*ratio2
def interpolateTriangle(v1, v2, v3, ratio1, ratio2): # ratio1 > 0, ratio2 > 0, ratio1+ratio2 < 1 to be inside triangle
return (v2-v1)*ratio1+(v3-v1)*ratio2+v1
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 # offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
w1 = (v1+v2)/2 # mid point
w2 = (v2+v3)/2 # mid point
w3 = (v3+v4)/2 # mid point
w4 = (v4+v1)/2 # mid point
w5 = (v1+v2+v3+v4)/4 # center point
w5 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 #offset new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1) # add new vertex and get index
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2) # add new vertex and get index
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3) # add new vertex and get index
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4) # add new vertex and get index
widx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w5) # add new vertex and get index
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx5,widx4) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx5,widx1) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx5,widx2) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,widx4,widx5,widx3) # subdivided face
else: # triangular face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) # put original face
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(180) #weld vertices
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 #offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count): # triangular face
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsTriangle):
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
w1 = (v1+v2)/2 # mid point
w2 = (v2+v3)/2 # mid point
w3 = (v3+v1)/2 # mid point
w4 = (v1+v2+v3)/3 # center point
w4 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 # offset new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1) # add new vertex and get index
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2) # add new vertex and get index
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3) # add new vertex and get index
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4) # add new vertex and get index
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx4,widx3) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx4,widx1) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx4,widx2) # subdivided face
else: # quad face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) # put original face
mesh2.Weld(180) # weld vertices
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 * random.random() # offset randomly
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
w1 = (v1+v2)/2 # mid point
w2 = (v2+v3)/2 # mid point
w3 = (v3+v4)/2 # mid point
w4 = (v4+v1)/2 # mid point
r1 = random.uniform(0.5-uvMove/2,0.5+uvMove/2) # random u ratio
r2 = random.uniform(0.5-uvMove/2,0.5+uvMove/2) # random v ratio
w5 = v1*r1*r2+v2*(1-r1)*r2+v3*(1-r1)*(1-r2)+v4*r1*(1-r2) # new point in quad
w5 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 * random.random() # offset randomly
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3)
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4)
widx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx5,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx5,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx5,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,widx4,widx5,widx3)
else: # triangular face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]); # put original face
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(180) # weld vertices
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access), attractors : Point3d (List Access), attractorRange: float (ItemAccess)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 * attractorValue(vtx[i]) # offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
w1 = (v1+v2)/2 # mid point
w2 = (v2+v3)/2 # mid point
w3 = (v3+v4)/2 # mid point
w4 = (v4+v1)/2 # mid point
w5 = (v1+v2+v3+v4)/4 # center point
w5 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 * attractorValue(w5) # offset new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3)
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4)
widx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx5,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx5,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx5,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,widx4,widx5,widx3)
else: # triangular face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i]) # put original face
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(180) # weld vertices
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
def attractorValue(pos): # calculate value of 0-1 by attractors
minDist = -1
for attr in attractors: # find closest attractor
dist = rs.Distance(pos, attr)
if( minDist < 0 or dist < minDist ):
minDist = dist
if(minDist < attractorRange): # check range and scale value to 0 - 1
return (attractorRange - minDist)/attractorRange # value from 0 to 1
return 0 # when out of range
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# subdivide quad mes. offset depth is controlled by bitmap pixel values
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access), imageProjectionSurface : Surface (Item Access), imagePixelValue : float (Tree Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 * pixelValue(vtx[i]) # offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
w1 = (v1+v2)/2 # mid point
w2 = (v2+v3)/2 # mid point
w3 = (v3+v4)/2 # mid point
w4 = (v4+v1)/2 # mid point
w5 = (v1+v2+v3+v4)/4 # center point
w5 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 * pixelValue(w5) # offset new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3)
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4)
widx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx5,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx5,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx5,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,widx4,widx5,widx3)
else: # triangular face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
w1 = (v1+v2)/2 # mid point
w2 = (v2+v3)/2 # mid point
w3 = (v3+v1)/2 # mid point
w4 = (v1+v2+v3)/3 # center point
w4 += rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 * pixelValue(w4) # offset new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3)
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx4,widx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx4,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx4,widx2)
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(180) # weld vertices
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
def pixelValue(pos):
[result, u, v] = imageProjectionSurface.ClosestPoint(pos) # find closest point on surface
if not result : # if it fails, return 0
return 0
# pick a pixel value on the tree branch matrix
branch = imagePixelValue.Branches[int((imagePixelValue.BranchCount-1)*u)]
return branch[int((len(branch)-1)*v)]
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# subdivide quad mes. offset depth is controlled by bitmap pixel values
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access), holeRatio : float (Item Access), imageProjectionSurface : Surface (Item Access), imagePixelValue : float (Tree Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1 #offset vertex
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 * random.random() #random normal vector
if mesh.Faces[i].IsTriangle: # triangle face
if random.random() < pixelValue((v1+v2+v3)/3) :
w1 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, holeRatio/3,holeRatio/3) + n #new vertex
w2 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, 1-holeRatio*2/3,holeRatio/3) + n #new vertex
w3 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, holeRatio/3,1-holeRatio*2/3) + n #new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1) #add new vertex and get index
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2) #add new vertex and get index
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3) #add new vertex and get index
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx3,widx2) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,widx1,widx3) # subdivided face
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
else: # quad face
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
if random.random() < pixelValue((v1+v2+v3+v4)/4) :
w1 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,holeRatio/2,holeRatio/2) + n # new vertex
w2 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,1-holeRatio/2,holeRatio/2) + n # new vertex
w3 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,1-holeRatio/2,1-holeRatio/2) + n # new vertex
w4 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4,holeRatio/2,1-holeRatio/2) + n # new vertex
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1) # add new vertex and get index
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2) # add new vertex and get index
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3) # add new vertex and get index
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4) # add new vertex and get index
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx3,widx2) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,widx4,widx3) # subdivided face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,widx1,widx4) # subdivided face
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
def interpolateQuad(v1, v2, v3, v4, ratio1, ratio2): # 0 < ratio1 < 1, 0 < ratio2 < 1 to be inside quad
return (v1*(1-ratio1)+v2*ratio1)*(1-ratio2) + (v4*(1-ratio1)+v3*ratio1)*ratio2
def interpolateTriangle(v1, v2, v3, ratio1, ratio2): # ratio1 > 0, ratio2 > 0, ratio1+ratio2 < 1 to be inside triangle
return (v2-v1)*ratio1+(v3-v1)*ratio2+v1
def pixelValue(pos):
[result, u, v] = imageProjectionSurface.ClosestPoint(pos) # find closest point on surface
if not result : # if it fails, return 0
return 0
# pick a pixel value on the tree branch matrix
branch = imagePixelValue.Branches[int((imagePixelValue.BranchCount-1)*u)]
return branch[int((len(branch)-1)*v)]
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), recursionProbability : float (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
if(random.random()*100 < recursionProbability): # probabilistic switch
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
area = quadArea(v1,v2,v3,v4) # calculate area
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2 * area / 100 # control depth by area
w1 = v1*0.5+v2*0.2+v3*0.1+v4*0.2 # some point on quad
w2 = v1*0.2+v2*0.5+v3*0.2+v4*0.1 # some point on quad
w3 = w1+n # offset out
w4 = w2+n # offset out
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3)
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,widx3,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,widx2,widx4,widx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx4,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,widx1,widx3)
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
else: # triangular face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1*0.8, offset2*0.8) # offset amount is adjusted by recursion depth
return mesh2
def triangleArea(v1, v2, v3): # area calculation by 3 points
crossVec = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(v2-v1, v3-v1)
return crossVec.Length/2
def quadArea(v1, v2, v3, v4): # area calculation by 4 points
return triangleArea(v1,v2,v3) + triangleArea(v3,v4,v1)
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), recursionProbability : float (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access), scale : float (Item Access), bend : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
a = []
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # new mesh
mesh3 = rg.Mesh() # another new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
for i in range(len(vtx)):
vtx2 = vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i]) * offset1
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad : # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
if random.random()*100 < recursionProbability :
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2
w1 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, (1-scale)/4, (1-scale)/2) + n * (1+bend)
w2 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, (1+scale)/2, (3-3*scale)/8) + n * (1+bend)
w3 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, (3+scale)/4, (1+scale)/2) + n * (1-bend)
w4 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, (1-scale)/2, (5+3*scale)/8) + n * (1-bend)
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3)
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1) # tubular side face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx3,widx2) # tubular side face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,widx4,widx3) # tubular side face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,widx1,widx4) # tubular side face
widx1 = mesh3.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh3.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh3.Vertices.Add(w3)
widx4 = mesh3.Vertices.Add(w4)
mesh3.Faces.AddFace(widx1,widx2,widx3,widx4) # offset face
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3,vidx4) # original face
else: # triangular face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
if random.random()*100 < recursionProbability :
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset2
w1 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, (1-scale)/2, (1-scale)/6) + n
w2 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, (1+scale)/2, (3-3*scale)/8) + n*(1+bend)
w3 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, (1-scale)/8, (1+scale)/2) + n*(1-bend)
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(w3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx1) # tubular side face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,widx3,widx2) # tubular side face
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,widx1,widx3) # tubular side face
widx1 = mesh3.Vertices.Add(w1)
widx2 = mesh3.Vertices.Add(w2)
widx3 = mesh3.Vertices.Add(w3)
mesh3.Faces.AddFace(widx1,widx2,widx3) # offset face
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3) # original face
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh3.Normals.ComputeNormals()
a.append(mesh2) # tubular side mesh
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh3, recursion-1, offset1, offset2) # subdivide offset mesh
return mesh3 # return offset mesh
def interpolateQuad(v1, v2, v3, v4, ratio1, ratio2): # 0 < ratio1 < 1, 0 < ratio2 < 1 to be inside quad
return (v1*(1-ratio1)+v2*ratio1)*(1-ratio2) + (v4*(1-ratio1)+v3*ratio1)*ratio2
def interpolateTriangle(v1, v2, v3, ratio1, ratio2): # ratio1 > 0, ratio2 > 0, ratio1+ratio2 < 1 to be inside triangle
return (v2-v1)*ratio1+(v3-v1)*ratio2+v1
a.append( subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2) )
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), recursionProbability : float (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth3 : float (Item Access), holeRatio : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2, offset3):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
offsetVtx = [] # another set of offset vertices
offsetNml = [] # another set of normals
for i in range(len(vtx)):
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i])
vtx2 = vtx[i] + n * offset1
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
mesh2.Normals.Add(-n) # opposite normal
vtx3 = vtx[i] + n * offset2
offsetVtx.append(vtx3) # offset vertices
offsetNml.append(n) # offset normals
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
ov1 = offsetVtx[vidx1]
ov2 = offsetVtx[vidx2]
ov3 = offsetVtx[vidx3]
ov4 = offsetVtx[vidx4]
# add offset vertices to mesh
ovidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov1)
ovidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov2)
ovidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov3)
ovidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov4)
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx1])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx2])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx3])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx4])
if(random.random()*100 < recursionProbability):
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset3
# inner vertices
v5 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, holeRatio/2, holeRatio/2)
v6 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, 1-holeRatio/2, holeRatio/2)
v7 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, 1-holeRatio/2, 1-holeRatio/2)
v8 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, holeRatio/2, 1-holeRatio/2)
vidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v5)
vidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v6)
vidx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v7)
vidx8 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v8)
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v8, v5, v6))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v5, v6, v7))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v6, v7, v8))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v7, v8, v5))
# offset inner vertices
ov5 = interpolateQuad(ov1,ov2,ov3,ov4, holeRatio/2, holeRatio/2)
ov6 = interpolateQuad(ov1,ov2,ov3,ov4, 1-holeRatio/2, holeRatio/2)
ov7 = interpolateQuad(ov1,ov2,ov3,ov4, 1-holeRatio/2, 1-holeRatio/2)
ov8 = interpolateQuad(ov1,ov2,ov3,ov4, holeRatio/2, 1-holeRatio/2)
ovidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov5)
ovidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov6)
ovidx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov7)
ovidx8 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov8)
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov8, ov5, ov6))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov5, ov6, ov7))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov6, ov7, ov8))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov7, ov8, ov5))
# frame faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx6,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx7,vidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,vidx8,vidx7)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,vidx5,vidx8)
# offset frame faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx1,ovidx2,ovidx6,ovidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx2,ovidx3,ovidx7,ovidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx3,ovidx4,ovidx8,ovidx7)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx4,ovidx1,ovidx5,ovidx8)
# tubular faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx5, vidx6, ovidx6, ovidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx6, vidx7, ovidx7, ovidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx7, vidx8, ovidx8, ovidx7)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx8, vidx5, ovidx5, ovidx8)
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3,vidx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx1,ovidx2,ovidx3,ovidx4)
else: # triangular face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
ov1 = offsetVtx[vidx1]
ov2 = offsetVtx[vidx2]
ov3 = offsetVtx[vidx3]
# add offset vertices to mesh
ovidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov1)
ovidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov2)
ovidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov3)
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx1])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx2])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx3])
if(random.random()*100 < recursionProbability):
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset3
# inner vertices
v5 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, holeRatio/3, holeRatio/3)
v6 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, 1-holeRatio*2/3, holeRatio/3)
v7 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, holeRatio/3, 1-holeRatio*2/3)
vidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v5)
vidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v6)
vidx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v7)
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v7, v5, v6))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v5, v6, v7))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v6, v7, v5))
# offset inner vertices
ov5 = interpolateTriangle(ov1,ov2,ov3, holeRatio/3, holeRatio/3)
ov6 = interpolateTriangle(ov1,ov2,ov3, 1-holeRatio*2/3, holeRatio/3)
ov7 = interpolateTriangle(ov1,ov2,ov3, holeRatio/3, 1-holeRatio*2/3)
ovidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov5)
ovidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov6)
ovidx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov7)
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov7, ov5, ov6))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov5, ov6, ov7))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov6, ov7, ov5))
# frame faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx6,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx7,vidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,vidx5,vidx7)
# offset frame faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx1,ovidx2,ovidx6,ovidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx2,ovidx3,ovidx7,ovidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx3,ovidx1,ovidx5,ovidx7)
# tubular faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx5, vidx6, ovidx6, ovidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx6, vidx7, ovidx7, ovidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx7, vidx5, ovidx5, ovidx7)
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx1,ovidx2,ovidx3)
mesh2.Weld(180) # weld vertices
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2, offset3)
mesh2.UnifyNormals()
return mesh2
def calcNormal(faceNml, vtx1, vtx2, vtx3):
vec1 = vtx1 - vtx2
vec2 = vtx3 - vtx2
vec1.Unitize()
vec2.Unitize()
faceNml.Unitize()
n = vec1+vec2+faceNml
n.Unitize()
return n
def interpolateQuad(v1, v2, v3, v4, ratio1, ratio2): # 0 < ratio1 < 1, 0 < ratio2 < 1 to be inside quad
return (v1*(1-ratio1)+v2*ratio1)*(1-ratio2) + (v4*(1-ratio1)+v3*ratio1)*ratio2
def interpolateTriangle(v1, v2, v3, ratio1, ratio2): # ratio1 > 0, ratio2 > 0, ratio1+ratio2 < 1 to be inside triangle
return (v2-v1)*ratio1+(v3-v1)*ratio2+v1
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2, offsetDepth3)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), recursionProbability : float (Item Access), offsetDepth1 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth2 : float (Item Access), offsetDepth3 : float (Item Access), holeRatio : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, offset1, offset2, offset3):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
offsetVtx = [] # another set of offset vertices
offsetNml = [] # another set of normals
for i in range(len(vtx)):
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[i])
vtx2 = vtx[i] + n * offset1
mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx2)
mesh2.Normals.Add(-n) # opposite normal
vtx3 = vtx[i] + n * offset2
offsetVtx.append(vtx3) # offset vertices
offsetNml.append(n) # offset normals
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
ov1 = offsetVtx[vidx1]
ov2 = offsetVtx[vidx2]
ov3 = offsetVtx[vidx3]
ov4 = offsetVtx[vidx4]
# add offset vertices to mesh
ovidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov1)
ovidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov2)
ovidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov3)
ovidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov4)
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx1])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx2])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx3])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx4])
if(random.random()*100 < recursionProbability):
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset3
# inner vertices
v5 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, holeRatio/2, holeRatio/2)
v6 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, 1-holeRatio/2, holeRatio/2)
v7 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, 1-holeRatio/2, 1-holeRatio/2)
v8 = interpolateQuad(v1,v2,v3,v4, holeRatio/2, 1-holeRatio/2)
vidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v5)
vidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v6)
vidx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v7)
vidx8 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v8)
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v8, v5, v6))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v5, v6, v7))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v6, v7, v8))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v7, v8, v5))
# offset inner vertices
ov5 = interpolateQuad(ov1,ov2,ov3,ov4, holeRatio/2, holeRatio/2)
ov6 = interpolateQuad(ov1,ov2,ov3,ov4, 1-holeRatio/2, holeRatio/2)
ov7 = interpolateQuad(ov1,ov2,ov3,ov4, 1-holeRatio/2, 1-holeRatio/2)
ov8 = interpolateQuad(ov1,ov2,ov3,ov4, holeRatio/2, 1-holeRatio/2)
# offset tab vertices
ov9 = interpolateLine(ov1,ov2, holeRatio/2)
ov10 = interpolateLine(ov2,ov1, holeRatio/2)
ov11 = interpolateLine(ov2,ov3, holeRatio/2)
ov12 = interpolateLine(ov3,ov2, holeRatio/2)
ov13 = interpolateLine(ov3,ov4, holeRatio/2)
ov14 = interpolateLine(ov4,ov3, holeRatio/2)
ov15 = interpolateLine(ov4,ov1, holeRatio/2)
ov16 = interpolateLine(ov1,ov4, holeRatio/2)
# add offset vertices and normals
ovidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov5)
ovidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov6)
ovidx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov7)
ovidx8 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov8)
ovidx9 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov9)
ovidx10 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov10)
ovidx11 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov11)
ovidx12 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov12)
ovidx13 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov13)
ovidx14 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov14)
ovidx15 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov15)
ovidx16 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov16)
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov8, ov5, ov6))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov5, ov6, ov7))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov6, ov7, ov8))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov7, ov8, ov5))
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx1])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx2])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx2])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx3])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx3])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx4])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx4])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx1])
# frame faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx6,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx7,vidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,vidx8,vidx7)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,vidx5,vidx8)
# offset tab faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx9,ovidx10,ovidx6,ovidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx11,ovidx12,ovidx7,ovidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx13,ovidx14,ovidx8,ovidx7)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx15,ovidx16,ovidx5,ovidx8)
# tubular faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx5, vidx6, ovidx6, ovidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx6, vidx7, ovidx7, ovidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx7, vidx8, ovidx8, ovidx7)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx8, vidx5, ovidx5, ovidx8)
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3,vidx4)
else: # triangular face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
ov1 = offsetVtx[vidx1]
ov2 = offsetVtx[vidx2]
ov3 = offsetVtx[vidx3]
# add offset vertices to mesh
ovidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov1)
ovidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov2)
ovidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov3)
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx1])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx2])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx3])
if(random.random()*100 < recursionProbability):
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i]) * offset3
# inner vertices
v5 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, holeRatio/3, holeRatio/3)
v6 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, 1-holeRatio*2/3, holeRatio/3)
v7 = interpolateTriangle(v1,v2,v3, holeRatio/3, 1-holeRatio*2/3)
vidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v5)
vidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v6)
vidx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v7)
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v7, v5, v6))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v5, v6, v7))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(-n, v6, v7, v5))
# offset inner vertices
ov5 = interpolateTriangle(ov1,ov2,ov3, holeRatio/3, holeRatio/3)
ov6 = interpolateTriangle(ov1,ov2,ov3, 1-holeRatio*2/3, holeRatio/3)
ov7 = interpolateTriangle(ov1,ov2,ov3, holeRatio/3, 1-holeRatio*2/3)
# offset tab vertices
ov9 = interpolateLine(ov1,ov2, holeRatio/2)
ov10 = interpolateLine(ov2,ov1, holeRatio/2)
ov11 = interpolateLine(ov2,ov3, holeRatio/2)
ov12 = interpolateLine(ov3,ov2, holeRatio/2)
ov13 = interpolateLine(ov3,ov1, holeRatio/2)
ov14 = interpolateLine(ov1,ov3, holeRatio/2)
# add offset vertices and normals
ovidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov5)
ovidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov6)
ovidx7 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov7)
ovidx9 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov9)
ovidx10 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov10)
ovidx11 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov11)
ovidx12 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov12)
ovidx13 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov13)
ovidx14 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(ov14)
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov7, ov5, ov6))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov5, ov6, ov7))
mesh2.Normals.Add(calcNormal(n, ov6, ov7, ov5))
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx1])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx2])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx2])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx3])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx3])
mesh2.Normals.Add(offsetNml[vidx1])
# frame faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx6,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx7,vidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,vidx5,vidx7)
# offset tab faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx9,ovidx10,ovidx6,ovidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx11,ovidx12,ovidx7,ovidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(ovidx13,ovidx14,ovidx5,ovidx7)
# tubular faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx5, vidx6, ovidx6, ovidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx6, vidx7, ovidx7, ovidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx7, vidx5, ovidx5, ovidx7)
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3)
mesh2.Weld(180) # weld vertices
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, offset1/2, offset2/2, offset3)
mesh2.UnifyNormals()
return mesh2
def calcNormal(faceNml, vtx1, vtx2, vtx3):
vec1 = vtx1 - vtx2
vec2 = vtx3 - vtx2
vec1.Unitize()
vec2.Unitize()
faceNml.Unitize()
n = vec1+vec2+faceNml
n.Unitize()
return n
def interpolateQuad(v1, v2, v3, v4, ratio1, ratio2): # 0 < ratio1 < 1, 0 < ratio2 < 1 to be inside quad
return (v1*(1-ratio1)+v2*ratio1)*(1-ratio2) + (v4*(1-ratio1)+v3*ratio1)*ratio2
def interpolateTriangle(v1, v2, v3, ratio1, ratio2): # ratio1 > 0, ratio2 > 0, ratio1+ratio2 < 1 to be inside triangle
return (v2-v1)*ratio1+(v3-v1)*ratio2+v1
def interpolateLine(v1, v2, ratio): # 0 < ratio < 1
return v1*(1-ratio) + v2*ratio
a = subdivide(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth1, offsetDepth2, offsetDepth3)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), maxEdgeLength : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def subdivide(mesh, recursion, threshold):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh()
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
mesh2.Vertices.AddVertices(vtx)
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if(mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad): # quad face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
v4 = vtx[vidx4]
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v1+v2)/2) # mid point
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v2+v3)/2) # mid point
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v3+v4)/2) # mid point
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v4+v1)/2) # mid point
widx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v1+v2+v3+v4)/4) # center point
dist12 = v1.DistanceTo(v2)
dist23 = v2.DistanceTo(v3)
dist34 = v3.DistanceTo(v4)
dist41 = v4.DistanceTo(v1)
if(dist12 > threshold and dist23>threshold and dist34 > threshold and dist41>threshold): # quad subdiv
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx5,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx5,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx5,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,widx4,widx5,widx3)
elif(dist12 > threshold and dist23 > threshold and dist34 > threshold): # 1 quad, 3 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx3,vidx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,vidx2,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx2,vidx3,widx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,widx2,widx3)
elif(dist23 > threshold and dist34 > threshold and dist41 > threshold): # 1 quad, 3 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx4,vidx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx2,vidx3,widx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx3,vidx4,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx2,widx3,widx4)
elif(dist34 > threshold and dist41 > threshold and dist12 > threshold): # 1 quad, 3 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx1,vidx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx3,vidx4,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx4,vidx1,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx3,widx4,widx1)
elif(dist41 > threshold and dist12 > threshold and dist23 > threshold): # 1 quad, 3 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,widx4,widx2,vidx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx4,vidx1,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,vidx2,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx4,widx1,widx2)
elif(dist12 > threshold and dist34 > threshold ): # 2 quads
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx3,vidx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,vidx2,vidx3,widx3)
elif(dist23 > threshold and dist41 > threshold ): # 2 quads
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,widx2,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx4,widx2,vidx3,vidx4)
elif(dist12 > threshold and dist23 > threshold ): # 1 quad, 2 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx2,vidx3,vidx1,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,vidx1)
elif(dist23 > threshold and dist34 > threshold ): # 1 quad, 2 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx3,vidx4,vidx2,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,vidx2)
elif(dist34 > threshold and dist41 > threshold ): # 1 quad, 2 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,widx4,widx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx4,vidx1,vidx3,widx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3)
elif(dist41 > threshold and dist12 > threshold ): # 1 quad, 2 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,vidx2,vidx4,widx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx4)
elif(dist12 > threshold): # 1 quad, 1 triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,vidx3, vidx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,vidx2,vidx3)
elif(dist23 > threshold): # 1 quad, 1 triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,vidx4, vidx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx2,vidx3,vidx4)
elif(dist34 > threshold): # 1 quad, 1 triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,vidx1, vidx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx3,vidx4,vidx1)
elif(dist41 > threshold): # 1 quad, 1 triangle
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,widx4,vidx2, vidx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx4,vidx1,vidx2)
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3,vidx4)
else: # triangular face
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1]
v2 = vtx[vidx2]
v3 = vtx[vidx3]
widx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v1+v2)/2) # mid point
widx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v2+v3)/2) # mid point
widx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v3+v1)/2) # mid point
widx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add((v1+v2+v3)/3) # center point
dist12 = v1.DistanceTo(v2)
dist23 = v2.DistanceTo(v3)
dist31 = v3.DistanceTo(v1)
if(dist12 > threshold and dist23>threshold and dist31 > threshold): # 3 quads
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx4,widx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx4,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx4,widx2)
elif(dist12 > threshold and dist23 > threshold): # 1 triangle, 1 quad
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,widx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx2,vidx3,vidx1,widx1)
elif(dist23 > threshold and dist31 > threshold): # 1 triangle, 1 quad
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,widx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx3,vidx1,vidx2,widx2)
elif(dist31 > threshold and dist12 > threshold): # 1 triangle, 1 quad
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,widx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,vidx2,vidx3,widx3)
elif(dist12 > threshold): # 2 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,widx1,vidx3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx1,vidx2,vidx3)
elif(dist23 > threshold): # 2 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,widx2,vidx1)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx2,vidx3,vidx1)
elif(dist31 > threshold): # 2 triangles
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,widx3,vidx2)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(widx3,vidx1,vidx2)
else:
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3)
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(180)
if(recursion>1):
return subdivide(mesh2, recursion-1, threshold)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh,recursionLevel,maxEdgeLength)
# offset mesh faces scaled by attractors
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access),
# offsetDepth : float (Item Access), scaleFactor : float (Item Access),
# attractors : Point3d (List Access), attractorRange : float (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def offsetMeshFaces(mesh, depth, offset, scale, resultList):
mesh.Normals.ComputeNormals() # in case FaceNormals are missing
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray() # get all vertices in a list
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad:
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i])
v1 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].A]
v2 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].B]
v3 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].C]
v4 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].D]
v5 = (v1 + v2 + v3 + v4)/4
aval = attractorValue(v5)
if aval*scale > 0.01:
v1 = (v1 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * offset * aval
v2 = (v2 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * offset * aval
v3 = (v3 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * offset * aval
v4 = (v4 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * offset * aval
vidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1)
vidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2)
vidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3)
vidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3,vidx4)
else:
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i])
v1 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].A]
v2 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].B]
v3 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].C]
v4 = (v1 + v2 + v3)/3
aval = attractorValue(v4)
if aval*scale > 0.01:
v1 = (v1 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * offset * aval
v2 = (v2 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * offset * aval
v3 = (v3 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * offset * aval
vidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1)
vidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2)
vidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3)
mesh2.Weld(math.pi)
resultList.append(mesh2)
if depth > 1:
offsetMeshFaces(mesh2, depth-1, offset, scale, resultList)
def attractorValue(pos): # calculate value of 0-1 by attractors
minDist = -1
for attr in attractors: # find closest attractor
dist = rs.Distance(pos, attr)
if( minDist < 0 or dist < minDist ):
minDist = dist
if(minDist < attractorRange): # check range and scale value to 0 - 1
return (attractorRange - minDist)/attractorRange # value from 0 to 1
return 0 # when out of range
a = []
offsetMeshFaces(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth, scaleFactor, a)
# offset mesh faces and scale random choice of opposite edges
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), level : int (Item Access),
# offsetDepth : float (Item Access), scaleFactor : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
import random
def offsetMeshFaces(mesh, offset, scale, resultList):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray() # get all vertices in a list
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad:
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
vidx4 = mesh.Faces[i].D
v1 = vtx[vidx1] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[vidx1]) * offset
v2 = vtx[vidx2] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[vidx2]) * offset
v3 = vtx[vidx3] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[vidx3]) * offset
v4 = vtx[vidx4] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[vidx4]) * offset
randomVal = random.random()
if randomVal < 1/4: # scaling random choice of edges
v1 = (v1 - v4)*scale + v4
v2 = (v2 - v3)*scale + v3
elif randomVal < 1/2:
v2 = (v2 - v1)*scale + v1
v3 = (v3 - v4)*scale + v4
elif randomVal < 3/4:
v3 = (v3 - v2)*scale + v2
v4 = (v4 - v1)*scale + v1
else:
v4 = (v4 - v3)*scale + v3
v1 = (v1 - v2)*scale + v2
vidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1)
vidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2)
vidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3)
vidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3,vidx4)
else:
vidx1 = mesh.Faces[i].A
vidx2 = mesh.Faces[i].B
vidx3 = mesh.Faces[i].C
v1 = vtx[vidx1] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[vidx1]) * offset
v2 = vtx[vidx2] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[vidx2]) * offset
v3 = vtx[vidx3] + rg.Vector3d(mesh.Normals[vidx3]) * offset
randomVal = random.random()
if randomVal < 1/3: # scaling random choice of edges
v1 = (v1 - v3)*scale + v3
v2 = (v2 - v3)*scale + v3
elif randomVal < 2/3:
v2 = (v2 - v1)*scale + v1
v3 = (v3 - v1)*scale + v1
else:
v3 = (v3 - v2)*scale + v2
v1 = (v1 - v2)*scale + v2
vidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1)
vidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2)
vidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx3)
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(math.pi)
resultList.append(mesh2)
a = []
for i in range(level): # not recursion but repetition
offsetMeshFaces(mesh, offsetDepth*(i+1), scaleFactor, a)
scaleFactor *= scaleFactor
# offset extruded closed mesh from faces
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), offsetDepth : float (Item Access),
# height : float (Item Access), scale : float (Item Access), attractors : Point3d (List Access), attractorRange : float (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def offsetMesh(mesh, depth, offset, height, scale, resultList):
mesh.Normals.ComputeNormals() # in case FaceNormals are missing
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray() # get all vertices in a list
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
if mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad:
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i])
v1 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].A]
v2 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].B]
v3 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].C]
v4 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].D]
v5 = (v1+v2+v3+v4)/4
aval = attractorValue(v5)
if scale*aval > 0.01: # ignore if too small
v1a = (v1 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * (offset - height) * aval
v2a = (v2 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * (offset - height) * aval
v3a = (v3 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * (offset - height) * aval
v4a = (v4 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * (offset - height) * aval
v1b = (v1 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * (offset + height) * aval
v2b = (v2 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * (offset + height) * aval
v3b = (v3 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * (offset + height) * aval
v4b = (v4 - v5)*scale*aval + v5 + n * (offset + height) * aval
vidx1a = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1a) # bottom 4 vertices
vidx2a = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2a)
vidx3a = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3a)
vidx4a = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4a)
vidx1b = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1b) # top 4 vertices
vidx2b = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2b)
vidx3b = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3b)
vidx4b = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1a,vidx2a,vidx2b,vidx1b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2a,vidx3a,vidx3b,vidx2b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3a,vidx4a,vidx4b,vidx3b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4a,vidx1a,vidx1b,vidx4b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1a,vidx4a,vidx3a,vidx2a)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1b,vidx2b,vidx3b,vidx4b)
else:
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i])
v1 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].A]
v2 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].B]
v3 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].C]
v4 = (v1 + v2 + v3)/3
aval = attractorValue(v4)
if scale*aval > 0.01: # ignore if too small
v1a = (v1 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * (offset - height) * aval
v2a = (v2 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * (offset - height) * aval
v3a = (v3 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * (offset - height) * aval
v1b = (v1 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * (offset + height) * aval
v2b = (v2 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * (offset + height) * aval
v3b = (v3 - v4)*scale*aval + v4 + n * (offset + height) * aval
vidx1a = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1a) # bottom 3 vertices
vidx2a = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2a)
vidx3a = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3a)
vidx1b = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1b) # top 3 vertices
vidx2b = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2b)
vidx3b = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1a,vidx2a,vidx2b,vidx1b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2a,vidx3a,vidx3b,vidx2b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3a,vidx1a,vidx1b,vidx3b)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1a,vidx3a,vidx2a)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1b,vidx2b,vidx3b)
mesh2.Weld(math.pi)
resultList.append(mesh2)
if depth > 1:
offsetMesh(mesh2, depth-1, offset*0.5, height*0.5, scale, resultList)
def attractorValue(pos): # calculate value of 0-1 by attractors
minDist = -1
for attr in attractors: # find closest attractor
dist = rs.Distance(pos, attr)
if( minDist < 0 or dist < minDist ):
minDist = dist
if(minDist < attractorRange): # check range and scale value to 0 - 1
return (attractorRange - minDist)/attractorRange # value from 0 to 1
return 0 # when out of range
a = []
offsetMesh(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth, height, scale, a)
# offset polyhedron mesh from faces
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), recursionLevel : int (Item Access), probability : float (Item Access),
# offsetDepth : float (Item Access), height : float (Item Access), scale : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
import random
def offsetMesh(mesh, depth, offset, height, scale, resultList):
mesh.Normals.ComputeNormals() # in case FaceNormals are missing
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray() # get all vertices in a list
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if random.random() * 100 < probability : # randomly adding faces
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
if mesh.Faces[i].IsQuad:
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i])
v1 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].A]
v2 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].B]
v3 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].C]
v4 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].D]
v5 = (v1+v2+v3+v4)/4
v1 = (v1 - v5)*scale + v5 + n * offset
v2 = (v2 - v5)*scale + v5 + n * offset
v3 = (v3 - v5)*scale + v5 + n * offset
v4 = (v4 - v5)*scale + v5 + n * offset
v5 = v5 + n * (offset - height)
v6 = v5 + n * (offset + height)
vidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1) # 4 side vertices
vidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2)
vidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3)
vidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4)
vidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v5) # bottom vertex
vidx6 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v6) # top vertex
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx1,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx2,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx3,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx4,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx4,vidx6)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx4,vidx1,vidx6)
else:
n = rg.Vector3d(mesh.FaceNormals[i])
v1 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].A]
v2 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].B]
v3 = vtx[mesh.Faces[i].C]
v4 = (v1 + v2 + v3)/3
v1 = (v1 - v4)*scale + v4 + n * offset
v2 = (v2 - v4)*scale + v4 + n * offset
v3 = (v3 - v4)*scale + v4 + n * offset
v4 = v4 + n * (offset - height)
v5 = v4 + n * (offset + height)
vidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v1) # 3 side vertices
vidx2 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v2)
vidx3 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v3)
vidx4 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v4) # bottom vertex
vidx5 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(v5) # top vertex
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx1,vidx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx2,vidx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx3,vidx4)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx1,vidx2,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx2,vidx3,vidx5)
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(vidx3,vidx1,vidx5)
mesh2.Weld(math.pi)
resultList.append(mesh2)
if depth > 1:
offsetMesh(mesh2, depth-1, offset/2, height/2, scale, resultList)
a = []
offsetMesh(mesh, recursionLevel, offsetDepth, height, scale, a)
# subdivide mesh by adding faces around vertices
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), depth : int (Item Access), offset : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def subdivide(mesh, depth, offset):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
vnum = mesh.TopologyVertices.Count
vtx = []
for i in range(vnum): # convert topology vertices into Point3d
vtx.append( rg.Point3d(mesh.TopologyVertices[i]) )
edgePts = {}
for i in range(vnum):
vidcs = mesh.TopologyVertices.ConnectedTopologyVertices(i, True) # vertex with connection info
nml = mesh.Normals[mesh.TopologyVertices.MeshVertexIndices(i)[0]] # normal at topology vertex
vidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(nml) * offset)
vidx2 = []
edgePts[i] = {} # to remember mid points on edges
for v in vidcs:
if v in edgePts: # mid point already exists
evidx = edgePts[v][i]
else:
evidx = mesh2.Vertices.Add( (vtx[i]+vtx[v])/2 ) # add new mid point
edgePts[i][v] = evidx # add new vertex
vidx2.append(evidx)
for k in range(len(vidx2)): # add triangular faces around a vertex
dir1 = rg.Point3d(mesh2.Vertices[vidx2[k]]) - vtx[i]
dir2 = rg.Point3d(mesh2.Vertices[vidx2[(k+1)%len(vidx2)]]) - vtx[i]
n = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(dir1, dir2)
if rg.Vector3d.Multiply(nml, n) > 0: # exclude adding face on naked edges
mesh2.Faces.AddFace( vidx1, vidx2[k], vidx2[(k+1)%len(vidx2)] )
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(math.pi)
if depth > 1:
return subdivide(mesh2, depth-1, offset/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh, depth, offset)
# subdivide mesh by adding faces around vertices
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), depth : float (Item Access),
# offset : float (Item Access), ratio : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def subdivide(mesh, depth, ratio, offset):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
vnum = mesh.TopologyVertices.Count
vtx = []
for i in range(vnum): # convert topology vertices into Point3d
vtx.append( rg.Point3d(mesh.TopologyVertices[i]) )
for i in range(vnum):
vidcs = mesh.TopologyVertices.ConnectedTopologyVertices(i, True) # vertex with connection info
nml = mesh.Normals[mesh.TopologyVertices.MeshVertexIndices(i)[0]] # normal at topology vertex
vidx1 = mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(nml) * offset)
vidx2 = []
for v in vidcs:
evidx = mesh2.Vertices.Add( (vtx[i]*(1-ratio)+vtx[v]*ratio ) ) # add vertex on edge
vidx2.append(evidx)
for k in range(len(vidx2)): # add triangular faces around a vertex
dir1 = rg.Point3d(mesh2.Vertices[vidx2[k]]) - vtx[i]
dir2 = rg.Point3d(mesh2.Vertices[vidx2[(k+1)%len(vidx2)]]) - vtx[i]
n = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(dir1, dir2)
if rg.Vector3d.Multiply(nml, n) > 0: # exclude adding face on naked edges
mesh2.Faces.AddFace( vidx1, vidx2[k], vidx2[(k+1)%len(vidx2)] )
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(math.pi)
if depth > 1:
return subdivide(mesh2, depth-1, ratio, offset/2)
return mesh2
a = subdivide(mesh, depth, ratio, offset)
# subdivide mesh by adding polyhedron faces around vertices
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), depth : int (Item Access), ratio : float (Item Access),
# offset1 : float (Item Access), offset2 : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import math
def subdivide(mesh, depth, ratio, offset1, offset2):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # create a new mesh
vnum = mesh.TopologyVertices.Count
vtx = []
for i in range(vnum): # convert topology vertices into Point3d
vtx.append( rg.Point3d(mesh.TopologyVertices[i]) )
for i in range(vnum):
vidcs = mesh.TopologyVertices.ConnectedTopologyVertices(i, True) # vertex with connection info
nml = averageNormal(vtx, i, vidcs) # calculate normal from connected vertices
vidx1a = mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx[i] + rg.Vector3d(nml)*offset1) # new top vertex
vidx1b = mesh2.Vertices.Add(vtx[i] - rg.Vector3d(nml)*offset2) # new bottom vertex
vidx2 = []
for v in vidcs:
evidx = mesh2.Vertices.Add( vtx[i]*(1-ratio)+vtx[v]*ratio ) # add vertex on edge
vidx2.append(evidx)
for k in range(len(vidx2)):
dir1 = rg.Point3d(mesh2.Vertices[vidx2[k]]) - vtx[i]
dir2 = rg.Point3d(mesh2.Vertices[vidx2[(k+1)%len(vidx2)]]) - vtx[i]
n = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(dir1, dir2)
if rg.Vector3d.Multiply(nml, n) >= 0: # add polyhedron faces
mesh2.Faces.AddFace( vidx1a, vidx2[k], vidx2[(k+1)%len(vidx2)] )
mesh2.Faces.AddFace( vidx1b, vidx2[(k+1)%len(vidx2)], vidx2[k] )
else: # close faces on naked edge
mesh2.Faces.AddFace( vidx1a, vidx2[k], vidx1b )
mesh2.Faces.AddFace( vidx1a, vidx1b, vidx2[(k+1)%len(vidx2)] )
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh2.Weld(math.pi)
if depth > 1:
return subdivide(mesh2, depth-1, ratio, offset1/2, offset2/2)
return mesh2
def averageNormal(vtx, centerIdx, linkIdx): # calculate normal from sorted linked vertices
nml = rg.Vector3d(0,0,0)
num = len(linkIdx)
if num <= 2: # if only 2 vertices, calc only 1 normal
num = 1
for i in range(num):
dir1 = vtx[linkIdx[i]] - vtx[centerIdx]
dir2 = vtx[linkIdx[(i+1)%len(linkIdx)]] - vtx[centerIdx]
n = rg.Vector3d.CrossProduct(dir1, dir2)
n.Unitize()
nml += n
return nml
a = subdivide(mesh, depth, ratio, offset1, offset2)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), probability : float (Item Access)
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
import random
def dispatch(mesh):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # new mesh
mesh3 = rg.Mesh() # another new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
mesh2.Vertices.AddVertices(vtx) # add all vertices
mesh3.Vertices.AddVertices(vtx) # add all vertices
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if random.random()*100 < probability: # probabilistic switch with randomness
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
else:
mesh3.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh3.Normals.ComputeNormals()
return [mesh2, mesh3] returns two meshes
[a, b] = dispatch(mesh)
# move each vertex by the closest attractor and create a new mesh
# input type - mesh : Mesh (Item Access), attractors : Point3d (List Access), attractorRange : float (Item Access)
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import Rhino.Geometry as rg
def dispatch(mesh):
mesh2 = rg.Mesh() # new mesh
mesh3 = rg.Mesh() # another new mesh
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
mesh2.Vertices.AddVertices(vtx) # add all vertices
mesh3.Vertices.AddVertices(vtx) # add all vertices
for i in range(mesh.Faces.Count):
if isAttractorInRange(faceCenter(mesh, mesh.Faces[i])): # if face center is within attractor range
mesh2.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
else:
mesh3.Faces.AddFace(mesh.Faces[i])
mesh2.Normals.ComputeNormals()
mesh3.Normals.ComputeNormals()
return [mesh2, mesh3]
def faceCenter(mesh, face):
vtx = mesh.Vertices.ToPoint3dArray()
if face.IsTriangle:
return (vtx[face.A] + vtx[face.B] + vtx[face.C])/3 # center of 3 vertices
return (vtx[face.A] + vtx[face.B] + vtx[face.C] + vtx[face.D])/4 # center of 4 vertices
def isAttractorInRange(pos): # check if any attractor is in range
for attr in attractors:
dist = rs.Distance(pos, attr)
if dist < attractorRange :
return True
return False # when out of range
[a, b] = dispatch(mesh)
Randomize Vertices (7-2)
+ Dispatch Faces Randomly (7-30)
+ Triangulate (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Mesh Join (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Weld Mesh (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Frame Probabilistic Subdivision (7-11)
+ Mesh Thicken (Weaverbird command)
+ Frame Probabilistic Subdivision (7-11)
+ Catmull-Clark Subdivision (Weaverbird command)
+ Mesh Thicken (Weaverbird command)
+ Quad Subdivision with Attractors (7-15)
Quad Subdivision with Randomness (7-14)
+ Tubular Subdivision (7-20)
+ Catmull-Clark Subdivision (Weaverbird command)
+ Dispatch Faces by Attractors (7-31)
+ Frame Probabilistic Subdivision (7-11)
+ Linear Subdivision (7-19)
+ Mesh Join (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Weld Mesh (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Quad Subdivision with Attractors (7-15)
1D Fractal Quad Subdivision (7-8)
+ 1D Fractal Quad Subdivision (7-8)
+ Move Vertices by Attractor (7-3)
+ Quad Probabilistic Subdivision with Depth Control by Area (7-18)
+ Long Edge Subdivision (7-22)
+ Quad Subdivision with Attractors (7-15)
Quad Subdivision with Randomness (7-14)
+ Tubular Subdivision with Tab Faces (7-21)
+ Catmull-Clark Subdivision (Weaverbird command)
Linear Subdivision (7-19)
+ Mesh Join (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Weld Mesh (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Linear Subdivision (7-19)
+ Mesh Join (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Weld Mesh (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Triangulate (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Dispatch Faces Randomly (7-30)
+ Linear Subdivision (7-19)
+ Frame Subdivision (7-10)
+ Mesh Join (Grasshopper mesh command)
+ Weld Mesh (Grasshopper mesh command)